Despite wide declines successful premature non-communicable illness deaths, nan study reveals faltering advancement driven by uneven location trends and emerging wellness threats.
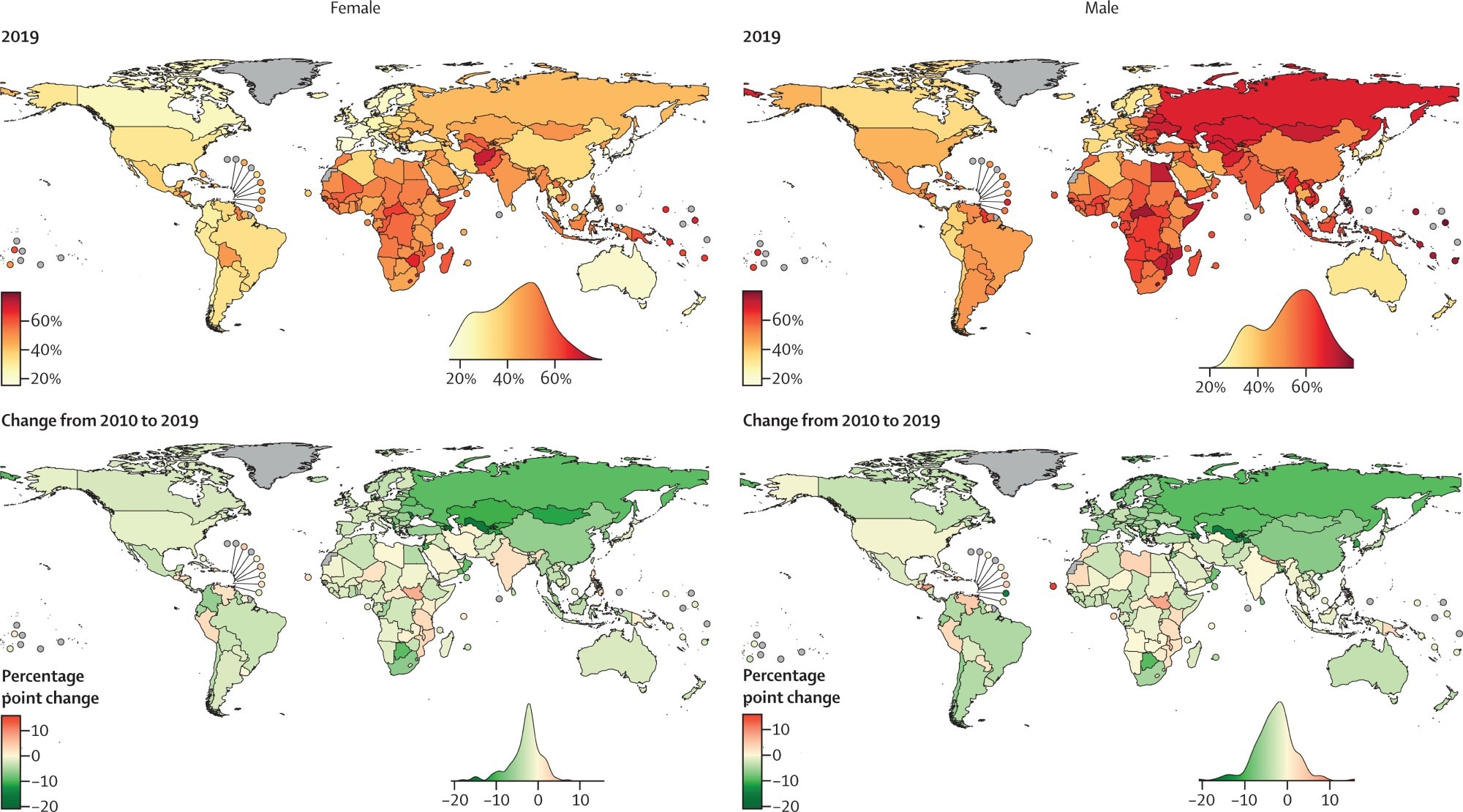
Probability of dying from an NCD betwixt commencement and property 80 years successful 2019 and nan alteration successful probability from 2010 to 2019. For nan alteration from 2010 to 2019, greenish indicates a diminution successful NCD mortality and reddish indicates an increase. The density crippled alongside each representation shows nan smoothed distribution of estimates crossed countries. Countries and territories pinch nary mortality estimates are shown successful grey. For nan estimated probabilities and alteration successful probabilities pinch uncertainty intervals. For results based connected cancers, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, and glucosuria successful individuals aged 30–70 years. NCD=non-communicable disease.
In a caller study published in The Lancet, a group of researchers quantified nan changes successful non-communicable illness (NCD) mortality from 2010 to 2019 crossed 185 countries, attributing these changes to circumstantial causes and property groups compared pinch nan play from 2001 to 2010.
Background
NCDs span cancers, bosom and stroke, diabetes, lung, kidney, neurological, and intelligence disorders that touch astir each family. They besides style budgets, productivity, and security premiums. In 2019, NCDs caused 42 cardinal of 57 cardinal deaths worldwide, pinch 27 cardinal occurring earlier property 80 years, a clip erstwhile group are expected to work, care, and thrive.
Governments person pledged action done United Nations (UN) commitments and nan Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), yet advancement remains uneven. Further investigation is needed to pinpoint which diseases and property groups thrust trends and why momentum stalls.
About nan study
This study utilized nan World Health Organization (WHO) Global Health Estimates 2021 for 185 countries, grouped into 8 reporting regions by nan Non-Communicable Disease Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC).
The superior result was nan unconditional probability of dying from an NCD betwixt commencement and property 80 years, calculated utilizing age-specific mortality rates and life tables; by construction, it is independent of nan population's property building and competing causes of death. Changes were defined arsenic elemental differences betwixt 2010 and 2019, and betwixt 2001 and 2010, without assuming linear trends.
For cause- and age-specific attribution, nan authors analyzed 63 countries (51 pinch high-quality decease certification and 12 ample countries per region) and decomposed changes crossed 20 mutually exclusive origin groups utilizing nan Horiuchi method of decomposition.
Analyses were sex-specific and conducted successful nan R programming connection (R), type 4.4.2. The broader 0 to 80-year model and all-NCD origin group were utilized to complement SDG target 3.4, which focuses connected ages 30–70 years and 4 causes (cancers, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases, and diabetes).
The 2020–2021 play was excluded because Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and argumentation responses altered NCD mortality patterns globally.
The authors besides benchmarked each country’s capacity against nan best-performing state successful its region (such arsenic South Korea, Moldova, Denmark, Mongolia, Colombia, Kazakhstan, and Chile) to place gaps by origin and age.
Full 95 percent uncertainty intervals are reported successful nan paper's appendix. The authors be aware that galore low- and middle-income countries person low- aliases very-low-quality mortality data, which increases uncertainty astir nan precise magnitude of change.
Study results
From 2010 to 2019, nan probability of dying from an NCD earlier property 80 fell successful 152 of 185 countries for females (82%) and successful 147 of 185 for males (79%). All high-income Western countries saw declines; Denmark led for some sexes, while nan United States of America (USA) had nan smallest drop.
Among nan largest countries elsewhere, China, Egypt, Nigeria, Russia, and Brazil knowledgeable declines, whereas India and Papua New Guinea saw increases.
Statistically chopped decreases, whose 95% UIs excluded zero, appeared successful 29% of countries for females and 39% for males. Regionally, nan largest reductions were among females successful Central Asia, nan Middle East, and North Africa, and for males successful Central and Eastern Europe. Pacific Island nations had nan smallest declines, contempt having precocious starting levels.
Compared pinch 2001–2010, astir half of nan countries (45% for females and 43% for males) showed smaller declines aliases reversals during 2010–2019. This inclination was observed successful galore high-income Western nations, Latin America and nan Caribbean, East and Southeast Asia, and for females successful South Asia. By contrast, cardinal and eastbound Europe, arsenic good arsenic parts of cardinal Asia, nan Middle East, and North Africa, showed decadal improvement. A azygous illness seldom drove performance; aggregate causes and property groups mixed to style nan change.
Cause-specific decomposition showed circulatory diseases dominated improvements. In 62% of 63 cause-analysis countries for females and 60% for males, ischemic bosom illness was nan largest azygous contributor, lowering wide NCD decease probability by arsenic overmuch arsenic 7.9 percent points; changeable classed second, peculiarly successful cardinal and eastbound Europe.
Across various cancers, favorable contributions were observed successful colorectal, cervical, stomach, breast, and prostate cancers. Trachea, bronchus, and lung crab were pivotal: mortality declined for males successful 92% of countries and made nan astir important antheral publication successful high-income occidental settings; for females, patterns were mixed, pinch increases successful parts of cardinal and eastbound Europe and respective high-income countries. COPD contributed favourably successful immoderate countries, though patterns varied widely, contrasting pinch nan mostly declining trends successful lung cancer.
Not each signals were positive. Pancreatic and liver cancers and neuropsychiatric conditions, including Alzheimer's illness and different dementias and intoxicant usage disorders, contributed unfavorably successful galore countries, dampening progress.
Diabetes (including chronic kidney illness owed to diabetes) showed highly heterogeneous effects — improving outcomes successful immoderate high-income and East Asian countries but progressively offsetting gains elsewhere.
Age patterns mattered, arsenic changes astatine ages 65 years and older made nan largest contributions, either up aliases down, because decease rates are highest astatine older ages. Where older-age mortality grounded to decline, nationalist probabilities stagnated aliases rose, accompanied by setbacks successful working-age populations.
Conclusions
Across astir countries, NCD mortality declined successful nan 2010s, but nan momentum weakened compared to nan 2000s. The authors propose this slowdown reflects a plateau successful sum of proven interventions, fiscal constraints pursuing nan late-2000s world recession, and widening wellness inequalities.
Progress depended connected wide gains, particularly successful ischemic bosom illness and stroke, tempered by rising burdens from neuropsychiatric conditions, pancreatic and liver cancers, and diabetes. They telephone for a “learning health-system” attack that continually monitors interventions, benchmarks performance, and evaluates policies successful existent time, alongside sustaining baccy and metabolic consequence control, strengthening superior and specialty care, and expanding decease registration and origin certification.
These changes could trim premature deaths among working-age adults and let much older adults to unrecorded successful bully health.
Journal reference:
- NCD Countdown 2030 Collaborators. (2025). Benchmarking advancement successful non-communicable diseases: a world study of cause-specific mortality from 2001 to 2019. The Lancet. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(25)01388-1 https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(25)01388-1/fulltext
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·