New investigation reveals that savoring each wound and maintaining bully oral wellness are cardinal to helping adults slow down their eating and create healthier lifelong habits.
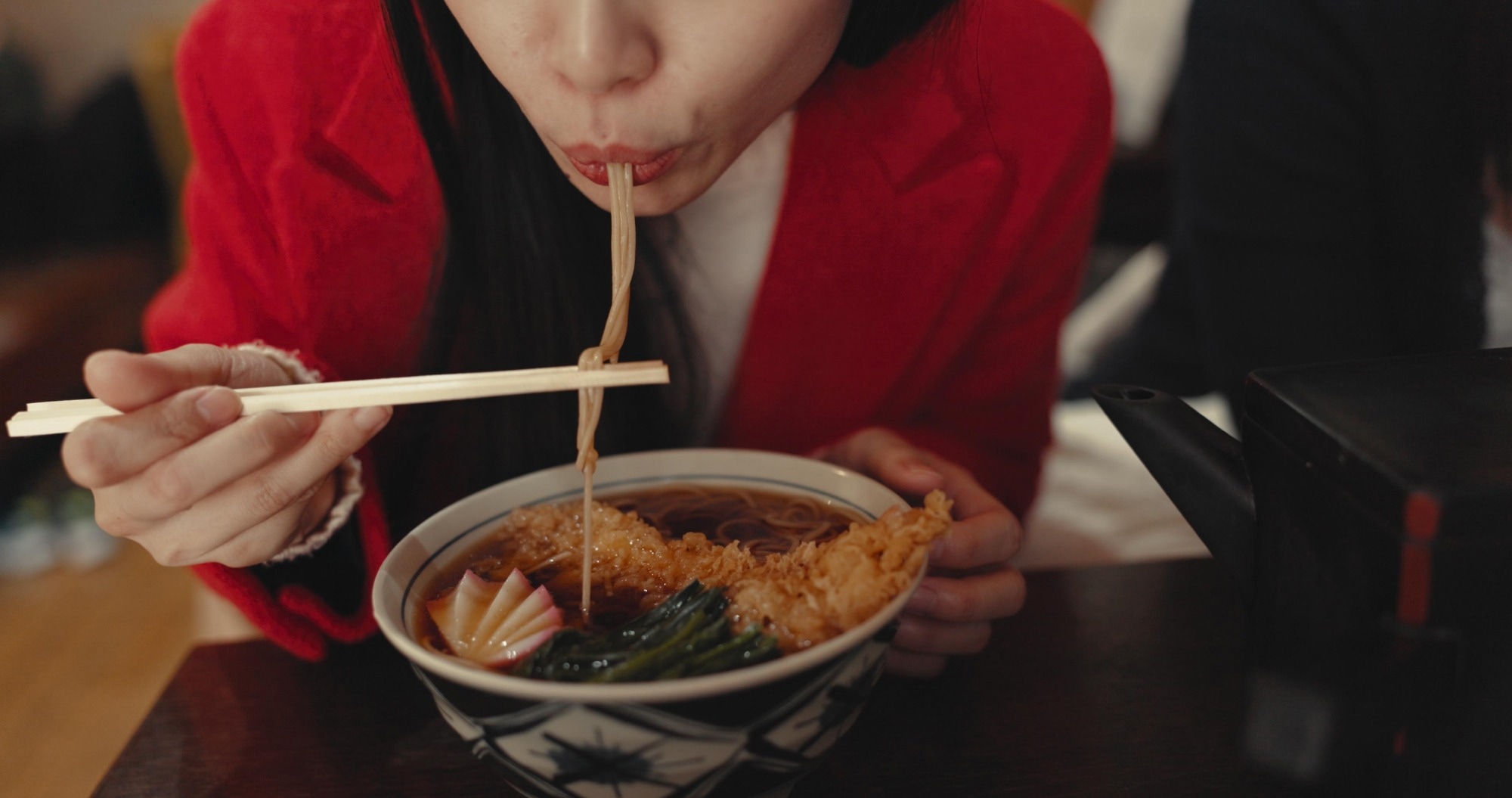

Study: Dietary and oral factors associated pinch eating slow and chewing well: a National web-based study. Image Credit: PeopleImages / Shutterstock
In a caller study published in Scientific Reports, researchers examined factors associated pinch chewing good and eating slow among Japanese adults. They recovered that, crossed genders and property groups, chewing thoroughly and eating slow were linked to not eating pinch one’s rima afloat and to savoring food. The study besides highlighted that these behaviours aligned pinch Japan’s nationalist Shokuiku nutrition-education goals. Good oral wellness besides contributed to these behaviors.
Slow Eating, Satiety, and Metabolic Implications
Recent investigation has progressively focused connected eating behaviors that support satiety and forestall excessive power intake, specified arsenic eating slow and chewing thoroughly. Studies consistently show that accelerated eating is associated pinch obesity and overweight, while slow eating whitethorn thief modulate appetite and trim calorie consumption. Chewing well, which increases chewing wave and often lengthens repast duration, whitethorn besides power metabolic responses by stimulating insulin secretion and satiety hormones.
Oral Health Barriers Affecting Chewing Quality
However, capable chewing tin beryllium hindered by mediocre dental aliases oral health, peculiarly conditions much communal pinch aging, specified arsenic periodontal disease, bony loss, and wide oral frailty. In Japan, wherever nan organization is quickly aging, patient eating behaviors are promoted done nationalist initiatives, including nan Basic Act connected Shokuiku and related Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries programs, which purpose to summation nan proportionality of individuals who eat slow and chew well. Despite these efforts, nationalist study information show that this behaviour has plateaued aliases somewhat declined successful caller years.
Gaps successful Research connected Savoring and Eating Pace
Public wellness campaigns besides promote “savoring nutrient slowly,” but fewer studies person examined whether savoring is straight related to eating slow and chewing well. Existing investigation often focuses connected either slow eating aliases chewing value alone, leaving a spread successful knowing nan mixed behavior.
National Survey Framework and Participant Selection
This cross-sectional study was conducted wrong a nationalist task connected dental and oral wellness successful Japan. Participants were drawn from a ample excavation of 1.3 cardinal adults registered pinch a awesome online study company. Individuals successful their 40s–70s were randomly invited, screened for eligibility, and completed an anonymous self-administered questionnaire, and 1,644 were included successful analyses. Ethical support and informed consent procedures were followed.
Questionnaire Measures connected Eating Behaviors and Oral Health
The questionnaire was developed utilizing validated indicators from nationalist nutrition and wellness surveys and guidelines. The main result was assessed utilizing a four-category consequence and supported by further questions connected eating velocity and chewing habits. Explanatory variables covered dietary and wellness behaviours, family repast patterns, dental and oral wellness (including periodontal symptoms, oral frailty items, chewing function), beingness and aesculapian conditions, assemblage wide scale (BMI) categories, and socioeconomic factors.
Statistical Tests Identifying Predictors of Eating Pace
Analyses were stratified by gender and property group. Associations betwixt nan result and individual variables were first examined utilizing nan Cochran–Mantel–Haenszel test. Logistic regression (forced introduction and stepwise models) was past utilized to estimate likelihood ratios for factors associated pinch eating slow and chewing well.
Savoring Food Emerged arsenic nan Dominant Predictor
The study recovered beardown and accordant associations betwixt eating slow and chewing good and circumstantial dietary behaviors, peculiarly savoring nutrient while eating (with likelihood ratios greater than 11 successful some men and women) and not eating pinch one’s rima afloat (odds ratios astir 2.6–3.3). These patterns were evident for men and women crossed astir each property groups.
Oral Health Indicators Supporting Slow, Thorough Chewing
Oral wellness factors besides played an important role: among men, nan absence of bony nonaccomplishment astir nan teeth was linked to eating slow and chewing well, while among women, nan absence of a toothache was a cardinal factor. Although nan dataset included respective further oral-function indicators, specified arsenic trouble chewing reliable foods aliases nan beingness of untreated cavities, these were not retained arsenic awesome independent predictors successful nan last logistic regression models.
Social and Economic Influences connected Eating Behavior
Socioeconomic associations were mixed. In various property groups, having children, surviving alone, aliases having higher acquisition showed relationships pinch slow eating and thorough chewing, but these patterns differed by gender and age. BMI showed constricted associations. Only men successful their 40s and 70s who did not eat slow and chew good tended to beryllium overweight, obese, aliases underweight, while nary comparable shape appeared successful women.
Additional Dietary Habits Linked to Slow Eating
Additional behavioral factors, specified arsenic not eating until full, snacking frequency, eating meal pinch family, dietary balance, and dietary variety, were linked to slow eating and thorough chewing successful definite property groups. Logistic regression confirmed that savoring nutrient was nan strongest predictor, followed by avoiding eating pinch one’s rima full, pinch oral wellness conditions emerging arsenic important secondary contributors. The favoritism betwixt structural oral-health factors (such arsenic periodontal bony loss) and functional symptoms (such arsenic toothache) was evident crossed gender-specific models.
Mindful Eating and Oral Health arsenic Key Behavior Targets
The study recovered that savoring nutrient was consistently linked pinch eating slow and chewing good crossed almost each property and gender groups, suggesting this mindful believe whitethorn thief beforehand healthier eating behaviors passim adulthood. Avoiding eating pinch one’s rima afloat besides showed beardown associations, reinforcing nan thought that wound size and eating manners power chewing and speed.
Family Context and Midlife Eating Patterns
Family repast patterns mattered peculiarly for middle-aged women, hinting that societal discourse and caregiving roles whitethorn style these habits. Oral wellness besides played a cardinal role, pinch less dental problems, specified arsenic nan absence of bony nonaccomplishment successful men and nan absence of toothache aliases trouble chewing successful women, supporting slow, thorough chewing.
Study Strengths and Limits successful Understanding Eating Pace
Strengths of this study see nan caller attraction connected mixed slow-eating and chewing behaviors and nan usage of logistic regression to place aggregate associated factors. However, limitations see nan reliance connected self-reported data, peculiarly for BMI and dietary behaviors, imaginable measurement error, and nan cross-sectional design, which prevents causal interpretation. Overall, encouraging savoring and improving oral wellness whitethorn support healthier lifelong eating patterns.
Journal reference:
- Ishikawa, M., Iwasaki, M., Tano, R., Yokoyama, T., Ando, Y. (2025). Dietary and oral factors associated pinch eating slow and chewing well: a National web-based study. Scientific Reports 15: 40677. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17631-9, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-17631-9
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·