A large-scale study of much than 3,600 group shows that reddish meat, erstwhile eaten arsenic portion of a balanced diet, tin heighten brain-supporting nutrients for illustration B12 and zinc without disrupting gut microbes aliases raising intelligence wellness risks.
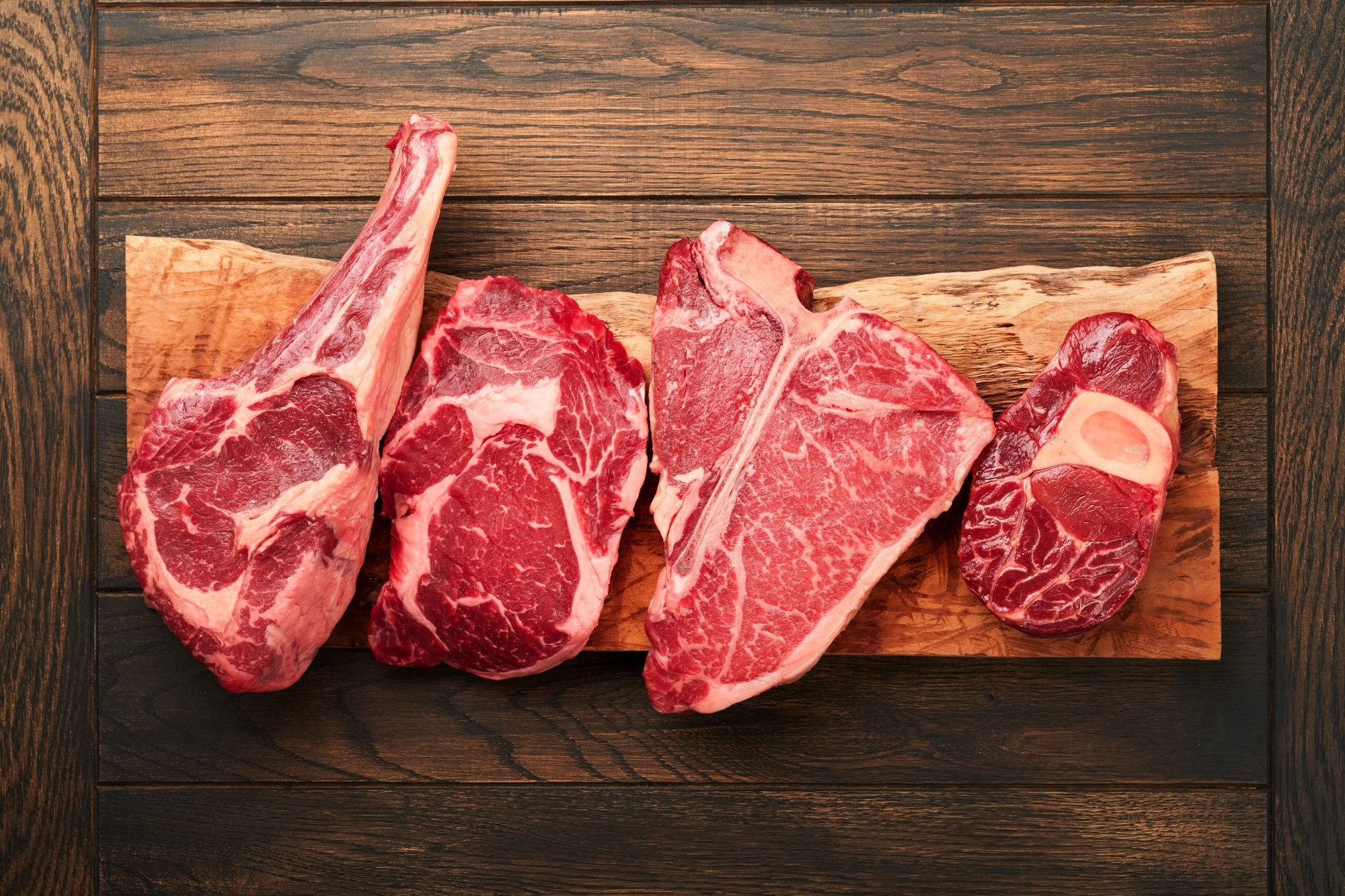 Study: Red nutrient depletion successful higher patient eating scale diets is associated pinch encephalon wellness captious nutritional adequacy, and fecal microbial diversity. Image credit: Katarzyna Hurova/Shutterstock.com
Study: Red nutrient depletion successful higher patient eating scale diets is associated pinch encephalon wellness captious nutritional adequacy, and fecal microbial diversity. Image credit: Katarzyna Hurova/Shutterstock.com
A caller study published successful Scientific Reports investigated whether reddish nutrient intake successful debased and precocious patient eating scale (HEI) diets is associated pinch fecal microbial diverseness creation and encephalon health-critical nutritional adequacy.
Diet has a important yet underrecognized domiciled successful intelligence health. A balanced fare pinch optimal levels of basal micronutrients, specified arsenic zinc, iron, folate, and vitamins B12 and D, is consistently associated pinch a little consequence of anxiety, cognitive decline, and depression. Deficiencies successful these micronutrients disrupt neurogenesis, signaling that regulates mood, cognition, and metabolic pathways. Red nutrient is simply a important root of micronutrients.
Red nutrient has faced scrutiny owed to associations pinch crab and cardiovascular disease. Nevertheless, studies person often grounded to relationship for fare value and differentiate unprocessed from processed meat. High-HEI diets are linked to a reduced consequence of intelligence wellness disorders; however, whether reddish nutrient successful HEI-matched diets improves micronutrient adequacy and supports intelligence wellness aliases fecal microbial diverseness has yet to beryllium evaluated.
About nan study
In nan coming study, researchers explored nan associations of reddish nutrient successful debased and high-HEI diets pinch micronutrient adequacy and fecal microbiota composition. They utilized information from nan American Gut Project (AGP), which recruited participants successful nan United States (US) and internationally. Participants provided fecal samples and completed metadata questionnaires.
Dietary intake accusation was collected utilizing nan nutrient wave questionnaire. Diet value was assessed utilizing nan 100-point HEI, comprising adequacy components (whole grains, full fruits, full macromolecule foods, and plant/seafood proteins) and moderation components (added sugars, sodium, refined grains). DNA was extracted from fecal samples.
The V4 region of nan 16S rRNA was amplified and sequenced. Mann-Whitney U-test and t-test were utilized to measure differences betwixt dietary groups. Shannon diverseness scale was utilized to analyse α-diversity; Bray-Curtis region and Jaccard scale were utilized to measure β-diversity. Linear discriminant study was performed to measure differential taxonomic abundance.
Findings
The study utilized information from 3,643 participants from nan AGP and stratified them into 4 groups based connected their reddish nutrient intake and HEI score. These groups were high-HEI pinch reddish nutrient (HH-R), low-HEI pinch reddish nutrient (LH-R), high-HEI without reddish nutrient (HH-NR), and low-HEI without reddish nutrient (LH-NR), pinch 319, 2,121, 325, and 878 participants, respectively. The HH-R group was marginally older than nan HH-NR group. Similarly, nan LH-R group was older than nan LH-NR group.
Further, HH-R participants showed a somewhat higher mean assemblage wide scale (BMI) than HH-NR subjects (23.8 vs 23.0), though some remained successful nan patient BMI range. Likewise, nan LH-R group had a higher mean BMI than nan LH-NR group. Of note, high-HEI groups had a little BMI than low-HEI groups. Further, macronutrient profiles were chopped betwixt HH-NR and HH-R groups, while power intake did not differ. On nan different hand, nan LH-R group had importantly higher power intake than nan LH-NR group.
Total carbohydrate intake was little successful HH-R and LH-R groups compared to HH-NR and LH-NR groups. Protein intake was higher successful LH-R and HH-R groups compared to LH-NR and HH-NR groups. Notably, dietary fibre intake was beneath capable levels successful each groups. In some low- and high-HEI groups, reddish nutrient consumers consistently had higher intakes of definite encephalon health-critical micronutrients than non-consumers.
Intake levels of vitamin B12, zinc, selenium, calcium, vitamin D, choline, and robust successful reddish nutrient consumers exceeded those of non-consumers. In contrast, folate intake was little successful reddish nutrient consumers than successful non-consumers. Notably, while vitamin D intake was importantly higher successful reddish nutrient consumers, it was beneath nan recommended levels successful each groups. Similarly, calcium intake was beneath nan recommended levels, pinch nan HH-R group approaching nan threshold.
Despite elevated intakes of circumstantial micronutrients among reddish nutrient consumers, depletion was beneath nan tolerable precocious intake level for astir everyone. Higher HEI scores were inversely associated pinch nan prevalence of virtually each neurodevelopmental and intelligence wellness disorders evaluated, including depression, bipolar disorder, and migraines. Significant inverse associations were besides recovered for attention-deficit/hyperactivity upset (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorder. Further, nan HH-R group exhibited nan highest phylum diversity, while nan LH-NR group had nan lowest.
There were nary differences successful α-diversity measures betwixt high-HEI groups. Conversely, nan LH-R group had importantly higher α-diversity than LH-NR. There were nary important differences successful β-diversity. However, differences successful nan comparative abundance of individual type were evident; nan HH-R group showed higher comparative abundance of Clostridium hathewayi and Bacteroides caccae, and nan HH-NR had higher abundance of Bacteroides eggerthii and Bifidobacterium adolescentis. The study besides reported shifts successful galore different bacterial taxa, including reductions successful immoderate Blautia, Roseburia, and Veillonella species among reddish nutrient consumers, arsenic good arsenic increases successful Collinsella aerofaciens.
Conclusions
Red nutrient intake wrong a high-HEI fare was associated pinch a modestly higher BMI but still wrong a patient scope and was not linked to adverse changes successful fecal microbiota. Instead, it was associated pinch improved micronutrient adequacy.
Both high-HEI groups had favorable macronutrient profiles, pinch reddish nutrient contributing to improved nutritional adequacy. Higher HEI was associated pinch a little prevalence of neurodevelopmental and intelligence wellness disorders, sloppy of reddish nutrient intake, pinch nan high-HEI fare preserving a favorable fecal microbial profile.
The authors be aware that nan cross-sectional design, self-selected sample, and imaginable reverse causation limit causal interpretation. They besides disclosed that nan National Cattlemen’s Beef Association funded nan study, though they had nary domiciled successful study creation aliases analysis.
Download your PDF transcript now!
Journal reference:
-
Dhakal S, Hossain M, Parajuli S (2025). Red nutrient depletion successful higher patient eating scale diets is associated pinch encephalon wellness captious nutritional adequacy, and fecal microbial diversity. Scientific Reports, 15(1), 33428. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-18907-w. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-18907-w
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·