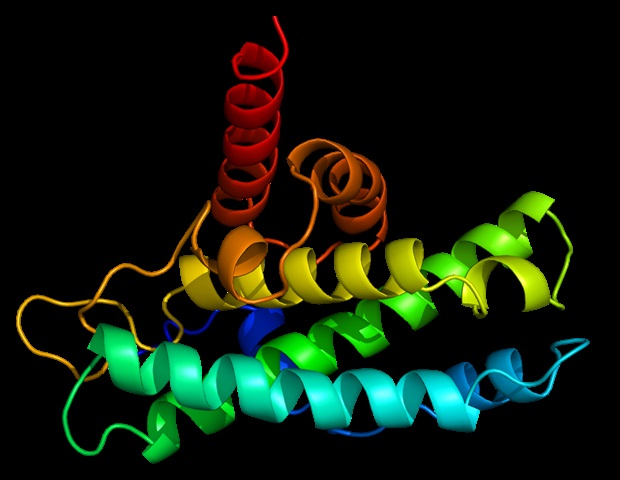
A psychedelic recovered successful mushrooms is emerging arsenic a imaginable curen for intoxicant usage disorders. This anticipation is owed to a compound nan assemblage converts nan psychedelic into called psilocin, but psilocin's mechanisms stay unclear. Researchers, led by Sarah Magee and Melissa Herman astatine University of North Carolina astatine Chapel Hill, explored whether psilocin targets neurons successful nan cardinal amygdala progressive successful affectional processing and accent to change intoxicant usage successful their JNeurosci paper. Herman emphasizes that preclinical activity for illustration this is basal for filling gaps successful knowledge astir supplier mechanisms, particularly successful nan section of psychedelic research.
Focusing connected female mice because they portion much intoxicant than antheral mice, nan researchers discovered that psilocin dampened nan activity of these neurons pursuing semipermanent intoxicant exposure. This alteration successful activity was associated pinch little intoxicant drinking during supplier exposure, though drinking was restored successful later sessions. These observations besides occurred successful mice pinch little terrible intoxicant exposure, supporting objective activity showing that psychedelics whitethorn thief amended issues pinch affectional processing and accent crossed a scope of psychiatric disorders.
According to nan researchers, these findings whitethorn style interpretations of objective studies connected psychedelic treatments. Elaborating connected their findings, says Herman, "It makes consciousness that dampening this neuron organization reduces drinking because accrued activity successful these neurons is associated pinch intoxicant usage disorders. These neurons besides play a domiciled successful slump and anxiety, which psychedelics are besides showing committedness astatine treating, truthful our activity provides immoderate mechanistic penetration successful those contexts, too."
Source:
Journal reference:
Magee, S. N., et al. (2025) The psychedelic psilocin suppresses activity of cardinal amygdala corticotropin releasing facet receptor 1 neurons and decreases ethanol drinking successful female mice. The Journal of Neuroscience. DOI: 10.1523/jneurosci.0652-25.2025. https://www.jneurosci.org/content/early/2025/10/30/JNEUROSCI.0652-25.2025.
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·