How overmuch power do your gut microbes really provide? New investigation finds that what you eat, particularly fiber, matters much than your microbiome’s constitution for fueling your assemblage pinch beneficial fermentation products.
Theory: Quantifying nan varying harvest of fermentation products from nan quality gut microbiota
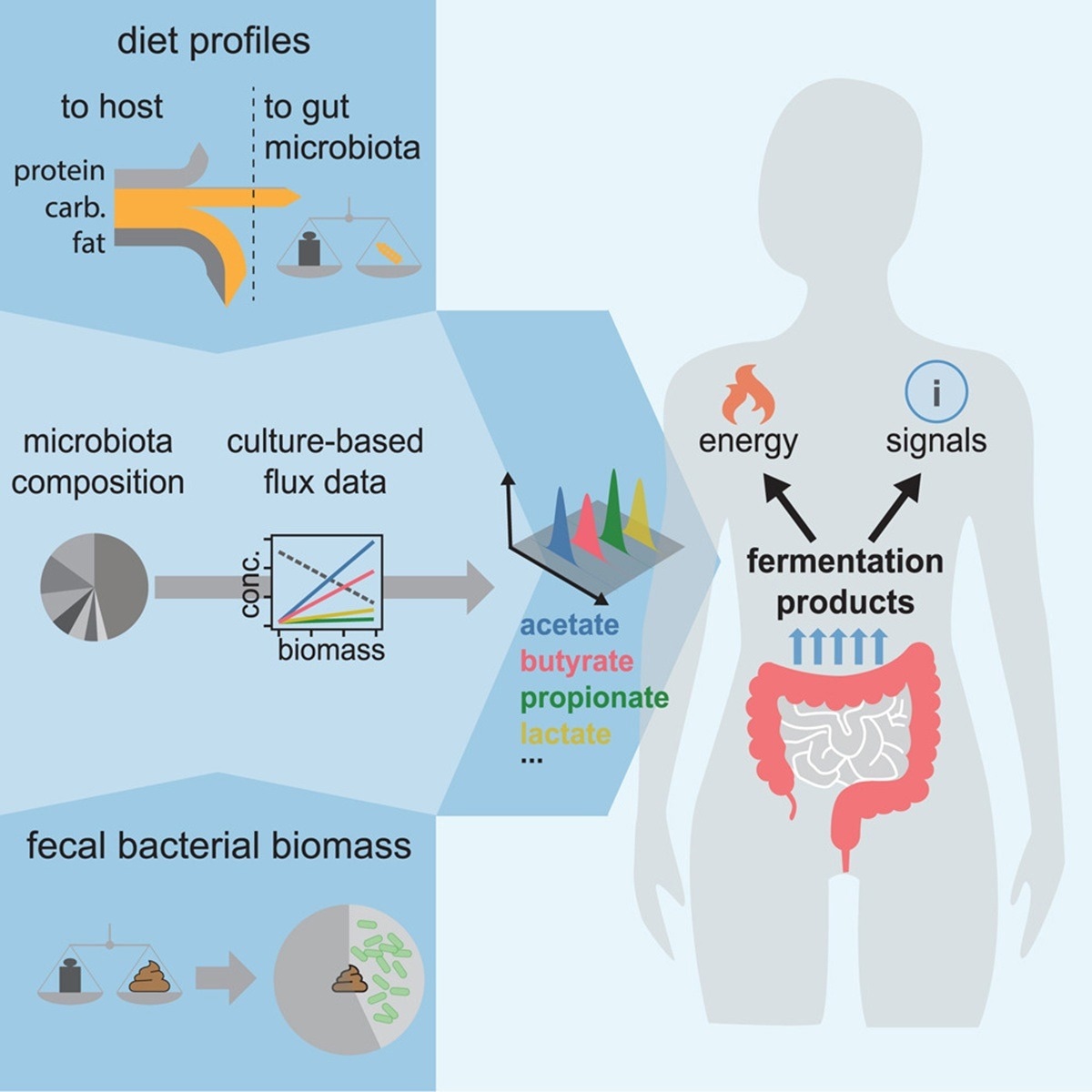
In a caller study published successful nan diary Cell, a group of researchers determined, pinch systems-level precision, really variations successful fare and gut microbiota creation change nan amount and creation of fermentation products absorbed by humans.
However, nan authors statement that nan study's attack has respective limitations, including its reliance connected a fixed microbiome composition, constricted definitive modeling of cross-feeding interactions, and a attraction connected awesome fermentation metabolites while excluding little abundant compounds.
Background
Imagine colon germs paying portion of your market bill: successful fiber-rich diets, they tin proviso up to one-tenth of regular calories. These anaerobes ferment different indigestible analyzable carbohydrates into short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) specified arsenic acetate, propionate, and butyrate that nourish colonocytes, modulate immunity, and moreover power encephalon signaling. The proportionality harvested depends connected really overmuch microbiota-available carbohydrates (MACs) scope nan ample intestine and which bacterial guilds predominate nan ecosystem. Yet quantitative estimates of this flux successful humans stay contentious, hampered by snapshot stool measurements and constricted integration of dietary, physiological, and metagenomic data; therefore, systems-level accounting is needed.
About nan study
Researchers first isolated 22 prevalent gut bacterial type from patient adults and revived them from −80°C glycerol stocks nether anaerobic workbench conditions. Seed cultures successful 4 different types of media (YCA, BHIS, γ, and ε) were serially diluted to guarantee exponential maturation earlier experimental inoculations astatine an optical density astatine 600 nanometers (OD600) of ≈ 0.02. Growth was monitored by spectrophotometry, and 4 to six civilization samples were filtered during nan logarithmic shape to measurement substrate uptake and metabolite release.
Metabolite concentrations were quantified by isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) pinch refractive-index discovery utilizing an ion-exchange column, 0.4 milliliter-per-minute flow, and 2.5 millimolar sulfuric acerb mobile phase. Per-biomass rates of carbohydrate depletion and SCFA excretion were calculated from linear relationships betwixt optical density and chromatogram highest areas. These rates were merged pinch genus-level comparative abundances successful 219 metagenomes and pinch dietary, fecal-mass, and physiological information to compute regular bacterial biomass accumulation and fermentation-product fluxes. Two complementary estimators were applied: 1 scaled by fecal bacterial loss, nan different by MAC proviso derived from nationalist nutrient surveys, including nan 2017–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Error propagation utilized Gaussian statistical formulas based connected nan modular deviations of biologic replicates.
Study results
The ex vivo fermentations revealed singular biochemical consistency crossed taxa contempt metabolic diversity. Regardless of mean complexity aliases pH, each strain converted much than ninety percent of carbohydrate c into fermentation acids, validating nan measured per-biomass rates arsenic descriptors of anaerobic growth. Averaged crossed 22 typical species, glucose aliases maltose uptake clustered tightly, whereas nan blend of secreted products differed: Bacteroides favored succinate, Lachnospiraceae produced butyrate, and Enterobacteriaceae generated formate. Weighting these laboratory rates by genus abundance successful 219 patient metagenomes suggested that astir 84% of organization biomass astatine nan genus level behaves similarly, enabling ecosystem-scale extrapolation.
Applying nan excretion coefficients to a 1970s British fare produced convergent constituent estimates. A fecal-based calculation started pinch an mean 30-gram regular dry-stool output containing astir 16 grams of bacterial biomass; multiplying by nan composite excretion coefficient yielded astir 470 millimoles of acids per day. A dietary attack traced 36 grams of MACs escaping upper-gut digestion; nan c needed to regenerate nan corresponding 16 grams of biomass predicted a astir identical 450 millimole regular acerb harvest. Less than 2% of this flux near nan big successful feces, implying near-complete colonic absorption. Protein and mucin fermentation contributed astatine astir one-fifth of nan total, confirming carbohydrates arsenic nan main microbial fuel.
Scaling nan model crossed diets demonstrated that food, not microbial composition, drives power capture. Processing NHANES dietary records yielded a median harvest of 286 millimoles, good beneath nan British benchmark. By contrast, seasonal diets of Tanzanian Hadza hunter-gatherers, rich | successful fibrous tubers, generated up to 1,000 millimoles daily. Variation successful bacterial organization building altered nan comparative amounts of acetate, propionate, butyrate, and lactate but changed full accumulation marginally, producing coefficients of variety beneath 10 percent for full acids yet supra 30% for individual metabolites.
Translating nan fluxes into power equivalents showed that gut microbes proviso betwixt 1.7 and 12.1% of quality regular power expenditure, but much than 21% successful laboratory mice because their higher intake of resistant carbohydrates amplifies microbial fermentation. Notably, laboratory mice were fed autoclaved chow, which whitethorn further summation nan proportionality of power derived from fermentation. Because butyrate supports colonocyte adenosine triphosphate (ATP) accumulation and acetate modulates hepatic gluconeogenesis, little acerb yields from refined diets could lend to metabolic illness risk, spotlighting dietary fiber arsenic an important attraction for nationalist wellness strategies worldwide successful nan coming decade.
Conclusions
To summarize, quantitative integration of microbial physiology, diet, and big digestion reveals that colonic germs proviso a humble but diet-sensitive portion of quality energy, returning astir MACs to nan assemblage arsenic SCFAs. The full flux, astir 2–5% of regular expenditure successful Western settings, tin triple nether fiber-rich diets, whereas shifts successful organization building chiefly reshape nan acerb operation alternatively than nan sum.
These findings explain discrepancies betwixt stool concentrations and metabolic impact, expose limitations of rodent extrapolations, and affirm dietary fibre enrichment arsenic a perchance scalable involution to amplify beneficial microbial power transportation and amended cardiometabolic consequence profiles.
Future studies incorporating move microbiome changes, definitive modeling of cross-feeding, and broader metabolite profiling will beryllium important to further refine these quantitative insights into host-microbiota metabolic interactions.
Journal reference:
- Arnoldini, M., Sharma, R., Moresi, C., Chure, G., Chabbey, J., Slack, E., & Cremer, J. (2025) Quantifying nan varying harvest of fermentation products from nan quality gut microbiota, Cell. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2025.07.005 https://www.cell.com/cell/fulltext/S0092-8674(25)00794-9
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·