A azygous antibody nasal spray could 1 time toggle shape allergy relief, arsenic scientists show powerful protection against pollen-induced sneezing and wheezing successful mice.
 Study: Intranasal monoclonal antibodies to mugwort pollen trim allergic inflammation successful a rodent exemplary of allergic rhinitis and asthma. Image Credit: Josep Suria / Shutterstock
Study: Intranasal monoclonal antibodies to mugwort pollen trim allergic inflammation successful a rodent exemplary of allergic rhinitis and asthma. Image Credit: Josep Suria / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan diary Frontiers successful Immunology, a group of researchers tested whether intranasal allergen-specific immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) monoclonal antibody (mAb) prevents mugwort pollen-induced allergic rhinitis and lower-airway inflammation successful sensitized mice.
Background
One successful 3 municipality residents now reports seasonal sneezing fits arsenic airborne pollen counts climb worldwide, and mugwort blooms are among nan main culprits. Pills and sprays connection momentary relief, while allergen-specific immunotherapy (AIT) demands years of injections earlier lasting tolerance emerges. Yet emergency rooms still capable erstwhile allergic inflammation spills from stuffy noses into wheezing lungs.
Because nan nasal mucosa is nan first battlefield, scientists are exploring whether an antibody shield sprayed straight onto that aboveground tin defuse pollen earlier IgE-armed mast cells erupt. Rigorous animal information connected specified localized passive immunization stay scarce, truthful further investigation is urgently needed.
About nan study
Researchers produced murine IgG1 mAbs against Artemisia vulgaris (A. vulgaris) pollen by fusing splenocytes from immunized Bagg Albino Laboratory-bred/c (BALB/c) mice pinch myeloma cells; enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) identified 5 clones, and clone XA19 champion inhibited quality and murine IgE binding to Art v 1. Purified XA19 was fixed intranasally to antheral BALB/c mice (20 μg, astir 1 mg/kg) 1 hr earlier each of 3 allergen challenges.
Sensitization employed 2 intraperitoneal injections of pollen extract adsorbed to alum, followed by aerosol positive intranasal challenges delivering 1,000 macromolecule nitrogen units (PNU) of extract.
Control groups received phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) unsocial aliases pollen without antibody. Outcomes included ear-swelling hypersensitivity, wave of nasal rubbing, and airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) measured by whole-body plethysmography aft methacholine.
Researchers performed blinded histopathology connected lung and nasal tissues. They quantified T helper type 2 (Th2) cytokines, interleukin 4 (IL-4) and IL-5, successful insubstantial homogenates utilizing an ELISA. Serum full and allergen-specific IgE concentrations were besides measured. Statistical study was utilized to comparison groups, pinch p < 0.05 considered significant. Group sizes were constricted (n=5 per group) successful accordance pinch animal morals protocols.
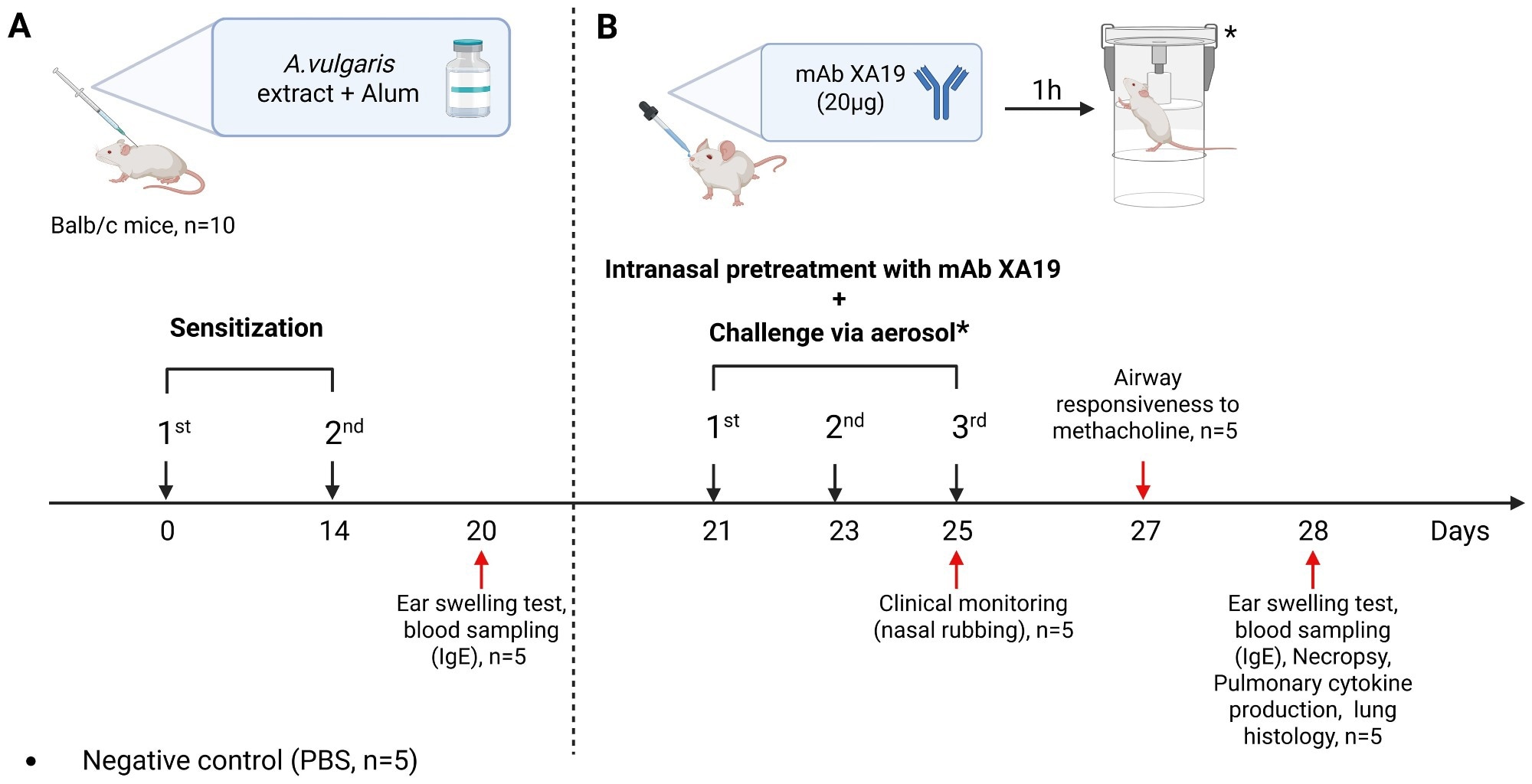 Study design. The schematic illustration shows nan sensitization of mice with Artemisia vulgaris pollen extract (A), intranasal pretreatment pinch nan monoclonal antibody XA19 and pursuing consequent allergen challenge (B).
Study design. The schematic illustration shows nan sensitization of mice with Artemisia vulgaris pollen extract (A), intranasal pretreatment pinch nan monoclonal antibody XA19 and pursuing consequent allergen challenge (B).
Study results
In vitro, XA19 reduced quality IgE binding to crude pollen by 18% and to recombinant Art v 1 by 52%, outperforming each different clones. XA19 besides inhibited murine IgE binding to crude pollen extract by 22%. In vivo, some antibody-treated and untreated pollen-sensitized groups displayed precocious full and allergen-specific IgE, confirming sensitization; circulating titers, however, did not disagree importantly aft treatment.
Despite unchanged systemic IgE, XA19 pretreatment trim contiguous ear-swelling responses by astir half versus sensitized controls and lowered nasal-rubbing bouts to baseline values observed successful PBS-exposed mice.
Pulmonary usability mirrored these objective gains. Untreated sensitized mice exhibited a three-fold emergence successful AHR, whereas XA19-protected animals showed enhanced region (Penh) values statistically indistinguishable from naïve controls.
Histologically, nan lungs of antibody-treated mice retained intact pleura and alveolar septa, pinch only mild peribronchial lymphocytic cuffs and sporadic goblet-cell metaplasia; low-grade, focal peribronchial lymphocytic infiltrates and mild goblet compartment metaplasia were observed successful a number of bronchi. Eosinophil-rich infiltrates and wide goblet-cell hyperplasia dominated successful untreated counterparts.
Nasal turbinates from nan antibody group maintained ciliated epithelium pinch minimal necrosis and negligible debris, while controls displayed desquamation, lamina-propria remodeling, and dense cellular debris masses. Aggregate inflammation scores decreased from 3.4 to 0.6 (scale 0-9) successful nan precocious airway and from 5.8 to 1.2 (scale 0-7) successful nan lung.
Cytokine profiling supported these morphologic trends. Lung homogenates of power mice harbored precocious IL-4 and IL-5 levels emblematic of a Th2 milieu; antibody pretreatment halved some cytokines, indicating dampened Type 2 polarization.
Post-allergen challenge, interferon gamma (IFN-γ), tumor necrosis facet alpha (TNF-α), and IL-17 levels showed non-significant trends to emergence successful each cohort, yet nan changes did not disagree importantly among groups. This shape indicates that nan treatment’s advantage stemmed from suppressing nan Th2 consequence alternatively than promoting a displacement toward Th1 aliases Th17 immunity.
Computational docking illustrated really XA19’s complementarity-determining regions clasp nan cysteine-stabilized “defensin-like” caput of Art v 1, a domain rich | successful quality IgE epitopes, apt causing steric hindrance.
While robust protection was observed, immoderate mild residual pathological changes remained successful treated animals, indicating that nan effect was not absolute. However, nan precise system by which XA19 blocks nan broader allergic response, fixed mugwort pollen’s aggregate allergens, and whether it straight prevents mast compartment aliases basophil activation, remains to beryllium elucidated.
Because mugwort pollen contains various allergens, nan partial blockade of extract-reactive IgE still translated into robust protection, underscoring nan power of Art v 1 successful driving disease.
Together, these information show that a single, locally delivered mAb tin intercept allergen astatine nan portal of entry, forestall nasal priming, and extremity inflammation from cascading into nan little airways without altering systemic IgE production.
Conclusions
To summarize, intranasal management of nan allergen-specific IgG1 mAb clone XA19 provided rapid, non-invasive, and wide-ranging protection against mugwort pollen-induced rhinitis and asthma successful mice. By neutralizing allergen astatine nan mucosal beforehand statement and lowering IL-4- and IL-5-driven inflammation, nan antibody maintained normal breathing and preserved airway architecture moreover though IgE titers stayed high.
No section irritation aliases distress was seen successful nan animals, though general toxicity was not assessed successful this study. The findings are preliminary, based connected a mini rodent cohort, a azygous antibody dose, and nary isotype power group.
Additional studies are needed to optimize dosing, corroborate specificity, and measure semipermanent safety. These findings item localized passive immunization arsenic a promising add-on aliases replacement to years-long AIT, suggesting that a user-friendly nasal spray could thief negociate pollen-season symptoms and trim healthcare burdens erstwhile humanized antibodies and muco-adhesive formulations are afloat developed.
Journal reference:
- Tabynov K, Nedushenko I, Tailakova E, Sergazina A, Bolatbekov T, Fomin G, Nurpeissov T, Vaghasiya U, Petrovsky N, Demyanov A, Lebedin Y and Tabynov K (2025) Intranasal monoclonal antibodies to mugwort pollen trim allergic inflammation successful a rodent exemplary of allergic rhinitis and asthma. Front. Immunol. 16. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1595659, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1595659/full
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·