A caller reappraisal shows really maternal microbes, beverage molecules, and modern lifestyles interact to style babies’ gut health, pointing to opportunities for prevention that span families and generations.

Review: Microbiome successful heritage: really maternal microbiome transmission impacts adjacent procreation health. Image Credit: Gorodenkoff / Shutterstock
In a caller reappraisal published successful nan journal Microbiome, researchers synthesized grounds connected really maternal intestinal bacteria, quality beverage components, and nan maternal situation power babe microbiome improvement and downstream risks for non-communicable diseases, highlighting preventive opportunities and investigation gaps.
Background
Within hours of birth, mini microbes statesman to settee successful a baby’s gut and turn quickly complete nan first years. What parents eat, really nan babe is born, really nan babe is fed, and which microbes and adjuvant molecules travel from nan mother each style this first community. Because overmuch of nan quality grounds is associative, animal studies person played a cardinal domiciled successful clarifying causality. These early choices tin thatch nan immune strategy to unrecorded peacefully pinch friends microbes aliases tin raise nan consequence of allergies, obesity, type 2 glucosuria mellitus, and inflammatory bowel illness later successful life. Modern surviving has lowered infections, but galore non-communicable diseases person increased. Further investigation is needed to construe this subject into a applicable and equitable prevention for each families.
Why nan First Microbes Matter
Early life is simply a highly integrative play during which nan infant's intestinal situation and microbiome create successful tandem. This crosstalk teaches nan immune strategy what to tolerate and what to fight. When improvement proceeds smoothly, immune tolerance is fostered; erstwhile it is disrupted, susceptibility to non-communicable diseases increases. These dynamics position early microbial exposures arsenic a powerful lever for semipermanent health. The reappraisal besides notes that early microbiome disruptions whitethorn impact antheral and female immune and metabolic outcomes differently.
Modern Lifestyles, New Pressures
Industrialization transformed diet, hygiene, and aesculapian care. While these advances reduced infectious diseases, they coincided pinch rising autoimmune diseases specified arsenic type 1 glucosuria mellitus and aggregate sclerosis, and pinch chronic inflammatory conditions including obesity, type 2 glucosuria mellitus, and inflammatory bowel disease. Growing grounds suggests that early-life disturbances successful host-microbiome interactions lend to this shift.
How Maternal Transmission Works
Maternal influences scope infants via 4 routes. During commencement and contact, maternal gut strains seed nan newborn. Human beverage oligosaccharides (HMOs) provender germs and nonstop metabolism. In mature milk, HMOs are coming astatine astir 5–20 g/L and scope nan babe gut mostly undigested to provender specialized taxa. Milk immunoglobulins, particularly secretory immunoglobulin A (IgA), positive antimicrobial peptides and metabolites style communities while training mucosal immunity. Colostrum contains nan highest SIgA concentrations, which diminution complete nan first period arsenic nan infant’s ain accumulation matures. Because beverage is low-biomass, results from beverage microbiota studies tin beryllium confounded by tegument aliases biology DNA. Maternal diet, medications, and exposures reconfigure nan maternal microbiome and molecular cargo delivered to infants.
Key pathways explicate these effects. Goblet cell-associated antigen transition (GAP) ferries antigens to immune cells, promoting tolerance. Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) prosecute G-protein-coupled receptors and epigenetic programs. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) ligands from diet-microbe interactions support obstruction integrity and immune balance.
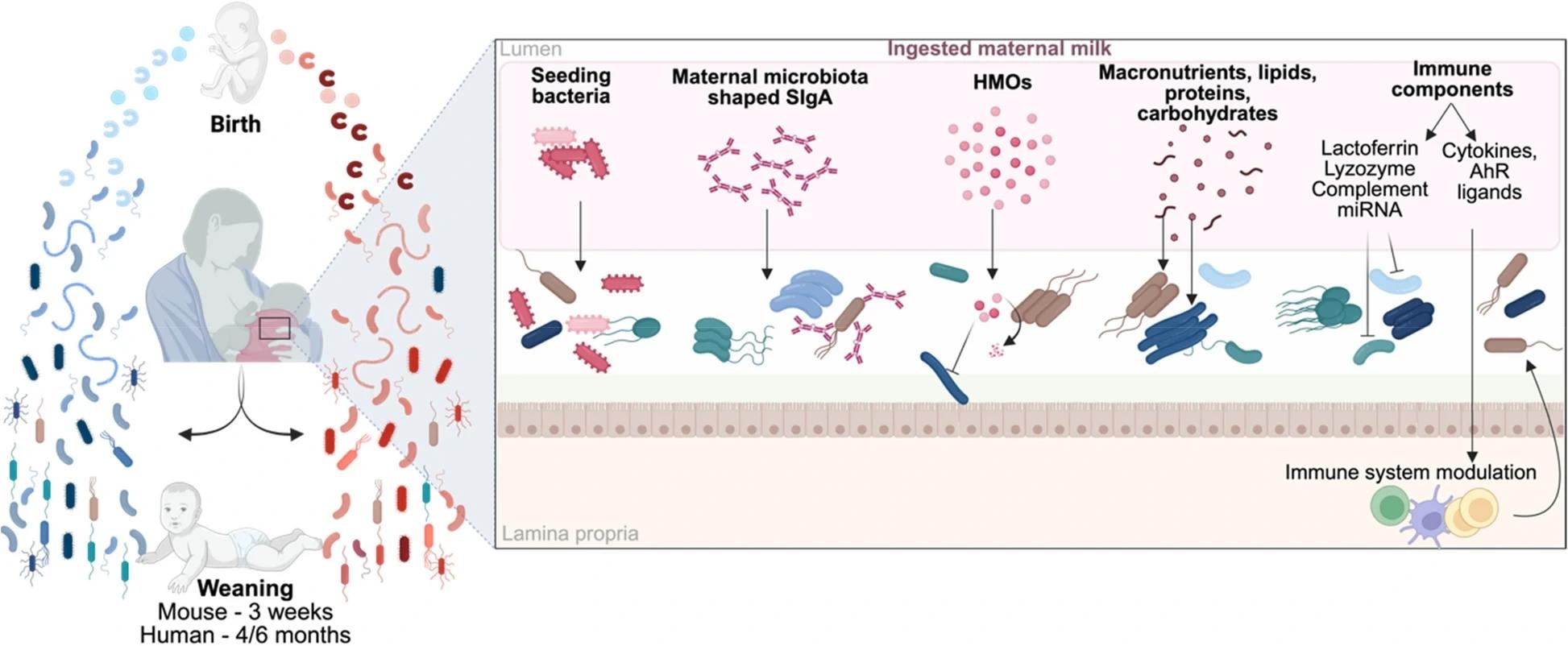
Impact of maternal beverage components connected microbiota establishment. Maternal beverage plays a important domiciled successful nan improvement of nan offspring's microbiota, providing a scope of components that power bacterial maturation and colonization. It contributes to nan infant’s microbiota by supplying bacteria, SIgA, HMOs, nutrients, and immune factors, which together beforehand aliases inhibit nan description of circumstantial bacterial populations done some nonstop and indirect mechanisms. The interplay of these factors shapes nan wide improvement of nan microbiota successful nan offspring. SIgA, secretory immunoglobulin A; HMOs, quality beverage oligosaccharides; miRNA, microRNA; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor
Feeding Choices and Microbial Trajectories
Breastfeeding delivers HMOs and secretory IgA that thrust a microbial floor plan associated pinch immune training. When breastfeeding is not imaginable aliases is mixed pinch formula, targeted innovations tin constrictive nan gap. In a objective study, babe look supplemented pinch 5 HMOs shifted microbiome creation and usability person to that of breastfed infants. Probiotic-enriched formulas tin besides modulate microbial communities and metabolic outputs. These approaches are promising, though nan durability of benefits and nan circumstantial taxa and pathways responsible still require meaning to guideline precise formulations.
Delivery, Antibiotics, and Early Perturbations
Mode of commencement and early antibiotic vulnerability tin perturb colonialism patterns. Population studies nexus cesarean transportation and babe antibiotics pinch higher risks of asthma, celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and moreover later metabolic alterations. The apt mediators see altered early colonizers, reduced transportation of beneficial maternal strains, and disrupted SCFA production. While causality tin beryllium complex, these findings underscore nan request for stewardship of perinatal antibiotics and support for microbial betterment erstwhile curen is necessary.
Maternal Diet: A Daily, Modifiable Lever
Maternal fare is simply a consistent, actionable power connected babe microbiome development. Diets precocious successful fibre proviso substrates for SCFA production, supporting epithelial wellness and immune tolerance. High-fat aliases ultra-processed patterns tin skew organization building and microbial metabolites toward inflammation. Evidence from quality cohorts and animal models shows that maternal dietary patterns reshape babe microbiota and immune programming, pinch effects that tin persist. Notably, interventions specified arsenic maternal fibre optimization and avoidance of definite additives whitethorn protect nan early microbial ecosystem, though findings for emulsifiers and non-nutritive sweeteners are chiefly preclinical.
Transgenerational Signals and Today’s Children
A striking penetration is that modern dietary shifts opening successful nan 1970s enforce some nonstop and transgenerational pressures. Today’s children whitethorn acquisition cumulative effects, resulting from their ain vulnerability to modern diets mixed pinch inherited influences from parental consumption, producing chopped phenotypes crossed generations. This conception reframes prevention arsenic family-wide and time-layered, not infant-only. Understanding and mitigating these pressures is basal for nationalist wellness strategies that sphere beneficial microbial ecosystems successful early life. While maternal transmission dominates, nan reappraisal concisely mentions that paternal microbiomes and fare whitethorn besides contribute, though this area remains exploratory.
From Mechanism to Prevention
Promising levers include: supporting breastfeeding wherever feasible, designing formulas pinch evidence-based HMOs and probiotics erstwhile needed, prudent perinatal antibiotic use, maternal dietary guidance emphasizing fiber-rich, minimally processed foods, and objective pathways that place and repair early microbiome disruptions. Translating mechanisms specified arsenic GAP-mediated antigen delivery, SCFA signaling, and AhR modulation into applicable interventions tin move attraction from reactive to preventive. Longitudinal tests that way microbial, immune, and objective outcomes are nan adjacent measurement successful confirming nan durability and equity of benefits crossed divers populations. Effects are apt to beryllium strain-, timing-, and context-specific, and precise targets stay to beryllium identified.
Conclusions
The reappraisal demonstrates that maternal microbial transfer, HMOs, IgA, and nan maternal situation collectively style babe microbiome trajectories, which power nan life consequence of allergies, obesity, type 2 glucosuria mellitus, and inflammatory bowel disease. Interventions specified arsenic breastfeeding support, evidence-based babe look design, dietary counseling during pregnancy, and observant antibiotic stewardship tin beforehand favorable colonialism and immune education. Because modern fare patterns exert cumulative, transgenerational pressures, prevention should span families and generations. Priority investigation includes long-term, divers tests that representation microbial functions to objective endpoints and trial scalable strategies to sphere early microbial ecosystems.
Journal reference:
- Delaroque, C., Chassaing, B. (2025). Microbiome successful heritage: really maternal microbiome transmission impacts adjacent procreation health. Microbiome 13. DOI: 10.1186/s40168-025-02186-8, https://microbiomejournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40168-025-02186-8
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·