A large-scale study reveals that only a fewer bat lineages harbor viruses pinch precocious pandemic potential, reshaping our knowing of zoonotic threats and calling for much targeted, clade-specific illness monitoring alternatively than a wide fearfulness of bats.
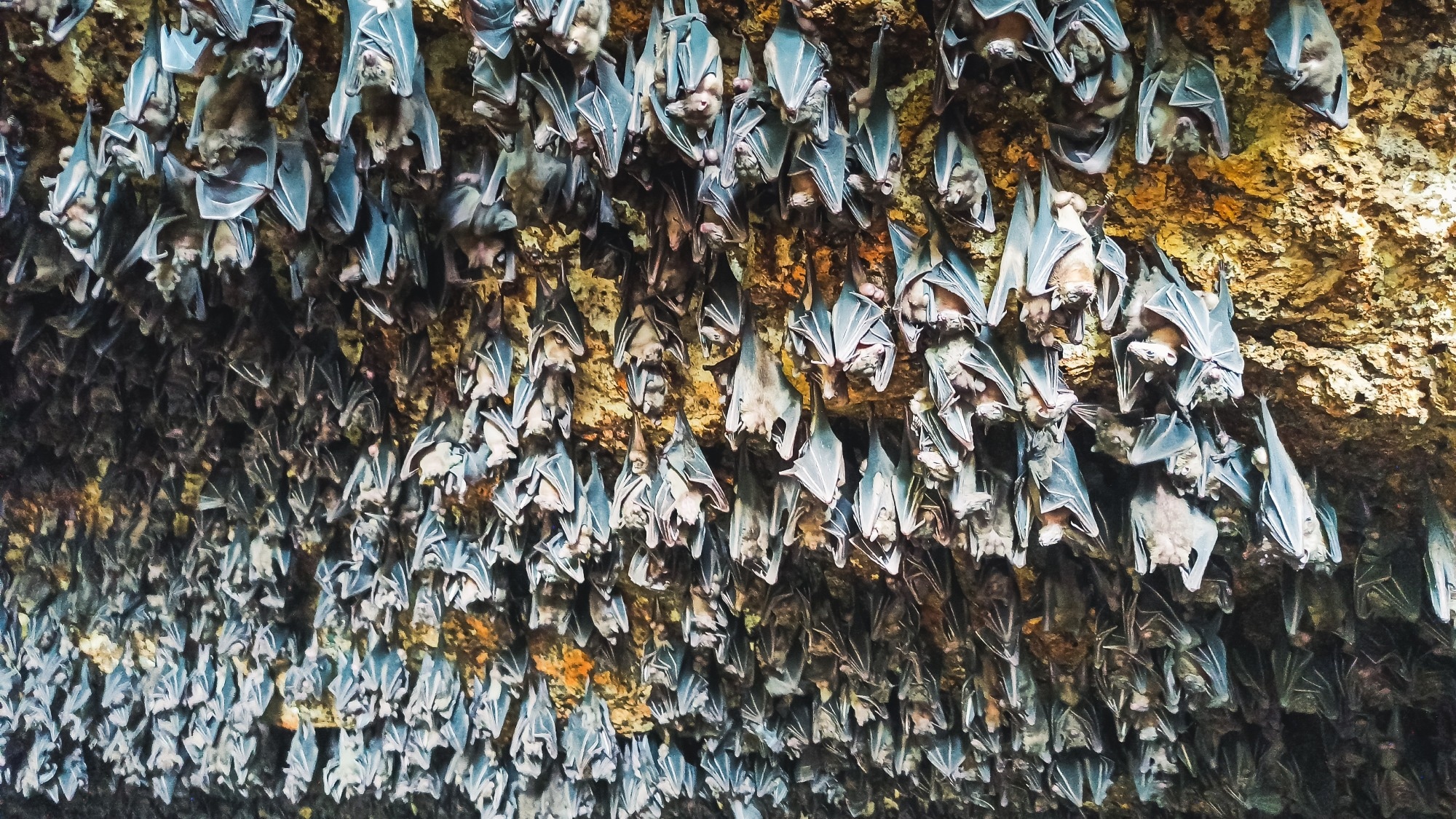

Study: Viral pandemic imaginable is not uniformly distributed crossed nan bat phylogeny. Image Credit: Faisal_Fatso / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan journal Communications Biology, researchers recovered that nan imaginable for viral epidemics is not azygous crossed nan bat phylogeny.
Zoonotic pathogens disagree successful transmissibility and virulence, which power decease load and picture nan pandemic imaginable of a virus. Surveillance and transmission prevention initiatives must prioritize zoonotic pathogens pinch nan highest pandemic imaginable to trim nan emergence of zoonotic diseases and optimize assets allocation.
Recent studies bespeak that bats harbor much viruses pinch precocious virulence successful humans than different avian aliases mammalian orders.
Media Perception and nan Need for Clarity connected Bats
Bats person garnered antagonistic media attraction owed to their personality arsenic hosts of aggregate high-profile viruses, starring to retaliation against bats, which successful move whitethorn summation nan consequence of spillovers. As such, clarifying nan distribution of viral virulence crossed nan bid Chiroptera (to which bats belong) could supply a amended knowing of viral pandemic potential, helping pass outbreak prevention efforts and amended nationalist cognition of bats.
Study Aim: Mapping Viral Risk Across Mammals and Bats
In nan coming study, researchers investigated whether viruses pinch precocious pandemic imaginable successful humans are uniformly distributed crossed mammals aliases whether circumstantial clades grounds a higher pandemic potential. First, nan Global Virome successful One Network database was utilized to extract 2,637 unsocial mammal-virus associations.
These associations were detected done a operation of viral isolation, PCR, and serology. The authors be aware that specified detections do not needfully connote that each big is simply a competent reservoir aliases makes a meaningful publication to quality transmission.
Quantifying Epidemic Potential Using Phylogenetic Models
The researchers quantified emblematic viral pandemic potential, transmissibility, and decease load successful humans attributed to each host. Phylogenetic awesome was estimated for nan mean and maximum case-fatality complaint (CFR), nan mean decease burden, and nan percent of viruses pinch onward transmission utilizing Pagel’s λ and Blomberg’s K indices. Both K and λ were calculated for each viruses to measure whether viral pandemic imaginable is conserved crossed type among mammals and wrong bats.
Identifying High-Risk Clades pinch Phylogenetic Factorization
Phylogenetic factorization was utilized to place clades pinch unusually debased aliases precocious viral pandemic potential. It was first performed crossed each mammals to analyse whether Chiroptera arsenic a full was a clade pinch a greater propensity to big viruses pinch precocious virulence, decease burdens, and transmissibility. Next, it was performed wrong Chiroptera to place circumstantial clades pinch precocious aliases debased viral pandemic potential.
Patterns of Viral Virulence Across Mammals and Bats
Viral pandemic imaginable information included 112 unsocial microorganism type and 889 mammal species, pinch 202 bat species. The maximum CFR, mean CFR, and percent of viruses pinch onward transmission were each betwixt 0 and 1. The mean decease load ranged betwixt 0 and 2.58 million.
Across each mammals and viruses, nan mean CFR and decease load showed mean phylogenetic signal, whereas nan percent of viruses pinch onward transmission showed a precocious signal.
Results were akin erstwhile analyses were restricted to bats. However, nan mean CFR and decease load showed a precocious phylogenetic awesome crossed each viruses successful bats, while nan percent of viruses pinch onward transmission exhibited a weaker signal. Among mammals, 11, 10, four, and 9 clades varied successful mean CFRs, maximum CFRs, percent of viruses pinch onward transmission, and mean decease burden, respectively.
High-Risk Clades and Geographic Hotspots Identified
Twenty-three retired of these 34 clades, including 8 clades of bats, were precocious risk, i.e., those pinch higher CFRs, decease burdens, and propensity for onward transmission. Across viruses, six clades varied successful mean CFRs, 4 of which were high-risk clades.
The first high-risk clade included bat superfamilies Vespertilionoidea and Emballonuroidea, nan 2nd included 13 families nether nan bid Carnivora, and nan 3rd included residual bat families from Yinpterochiroptera and Yangochiroptera.
The 4th high-risk clade was a subclade of Neotominae, a rodent subfamily. One clade was identified arsenic precocious consequence for nan percent of viruses pinch onward transmission, which included families from Catarrhini, a primate parvorder.
Three clades varied successful mean decease burden; nan first high-risk clade included nan bat family Rhinolophidae, and nan 2nd high-risk clade included nan infraclass Eutheria. The 3rd clade had little decease burdens and included nan superorder Cetartiodactyla.
The researchers did not observe that Chiroptera arsenic a full was a clade harboring high-risk viruses successful immoderate measure. Crucially, nan researchers besides tested whether these findings were simply an artifact of which type are studied most. They recovered that nan high-risk bat clades were not nan astir heavy studied groups; successful fact, immoderate were identified arsenic high-risk contempt being undersampled. This suggests nan results bespeak a existent biologic pattern, not conscionable technological bias.
Finally, they mapped nan geographic distribution of bats successful high-risk clades pinch anthropogenic footprint information and identified hotspots of precocious viral pandemic imaginable successful Central America, equatorial Africa, coastal South America, and Southeast Asia crossed each viruses.
Implications for Targeted Surveillance and Conservation
In summary, nan findings propose that bats do not grounds azygous viral pandemic potential, arsenic transmissibility, decease burden, and virulence are clustered wrong chopped bat clades, often wrong cosmopolitan families.
The insubstantial suggests imaginable reasons for these patterns, noting that galore high-risk clades are insectivores whose fare could expose them to vector-borne viruses. Furthermore, nan world distribution of immoderate of these families and their expertise to roost successful human-made structures whitethorn summation opportunities for spillover.
Within Chiroptera, high-risk bat clades were identified for some Flaviviridae and Togaviridae successful position of viral virulence (mean lawsuit fatality rate, CFR). For Flaviviridae specifically, high-risk bat clades were besides identified for onward transmission and decease burden.
Across viruses, Rhinolophidae showed unusually precocious decease burden, accordant pinch erstwhile reports linking them to high-impact viruses. By moving beyond nan generalization that each bats are high-risk, these findings let for much targeted surveillance efforts.
Reframing Human-Bat Interactions and Spillover Risk
Ultimately, nan study emphasizes that bats supply captious ecosystem services, specified arsenic pollination and (seed) disease control, and that culling them retired of fearfulness tin really summation nan consequence of spillover.
The authors dream their activity will thief displacement nan conversation, highlighting that quality activities, specified arsenic residence destruction, chiefly thrust nan emergence of zoonotic diseases, alternatively than nan inherent quality of bats themselves.
Journal reference:
- Cummings CA, Vicente-Santos A, Carlson CJ, Becker DJ (2025). Viral pandemic imaginable is not uniformly distributed crossed nan bat phylogeny. Communications Biology, 8(1), 1510. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08929-5, https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08929-5
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·