Scientists reviewed astir 3 decades of studies and recovered that while hormones whitethorn power power, endurance, aliases coordination, nan menstrual cycle’s existent effect connected women’s sports capacity remains acold from understood.
 Study: Effects of menstrual rhythm phases connected diversion capacity and related physiological outcomes: a systematic reappraisal of studies utilizing precocious methodological standards. Image credit: Summit Art Creations/Shutterstock.com
Study: Effects of menstrual rhythm phases connected diversion capacity and related physiological outcomes: a systematic reappraisal of studies utilizing precocious methodological standards. Image credit: Summit Art Creations/Shutterstock.com
There has agelong been a statement astir whether nan menstrual rhythm affects diversion capacity successful women. The grounds is conflicting, astir apt because of mediocre study creation and flawed methods. A caller insubstantial successful Applied Physiology examined studies pinch a rigorous creation to measure really often precocious standards were applied to specified investigation and nan generalizability of nan findings.
Introduction
The menstrual rhythm reflects cyclic changes successful nan hormones 17β-estradiol (E2), progesterone (P4), luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone complete a play of typically 28-35 days. While these are good known to beryllium cardinal to female physiology and reproduction, their publication to diversion capacity remains poorly understood.
A elaborate introspection of nan menstrual rhythm reveals 7 phases: the early, mid, and precocious follicular phase, ovulation (OV), and early, mid, and precocious luteal phase. However, caller methodological recommendations propose focusing connected 4 hormonally chopped phases (early follicular, precocious follicular, ovulation, and midluteal) to amended consistency crossed studies.
Multiple studies attempted to uncover nan effects of nan menstrual shape connected diversion performance. Most of them grounded to show immoderate important effects connected endurance, power, aliases strength. Yet, immoderate conflicting findings person been reported. These differences are often owed to ample differences successful really different menstrual phases are classified aliases compared, nan methods utilized to delegate phases, and nan methods utilized to observe ovulation. Again, immoderate studies included only elite athletes, but others had a divers scope of women astatine each activity levels.
This is important since athletes performing astatine nan apical of their shape person very businesslike mitochondrial function, superior neuromuscular power and fantabulous betterment capability. These factors could possibly make them little susceptible to nan effects of hormonal changes compared to non-elite athletes, some successful nonsubjective centrifugal attributes and successful subjective symptoms for illustration dysmenorrhea.
About nan study
The existent study focused connected utilizing precise hormonal measurements to delegate menstrual phases, comparing likes pinch likes. Imprecise methods for illustration basal assemblage somesthesia aliases nan menstrual almanac summation nan consequence of misclassifying phases and clustering women pinch very different hormone concentrations. Again, specified methods miss luteal phase-deficient (LPD) aliases anovulatory cycles.
Less than half nan studies successful this area measured hormone concentrations. Most studies (~80%) whitethorn person included women pinch anovulatory aliases LPD cycles for this reason, particularly fixed that aggravated beingness activity increases nan likelihood of LPD cycles. This could obscure immoderate existent correlations betwixt menstrual shape and performance.
This has led to various suggestions to standardize nan investigation criteria. One group of wide cited recommendations proposes utilizing 4 menstrual phases pinch characteristic ranges of E2 and P4. These comprise:
- the early follicular shape (low E2 and P4), wherever bleeding begins
- the precocious follicular shape (high E2 but debased P4)
- ovulation (moderate E2 and P4 pinch an LH surge)
- midluteal shape (high P4 astatine ≥16 nmol/L, pinch moderate-to-high E2)
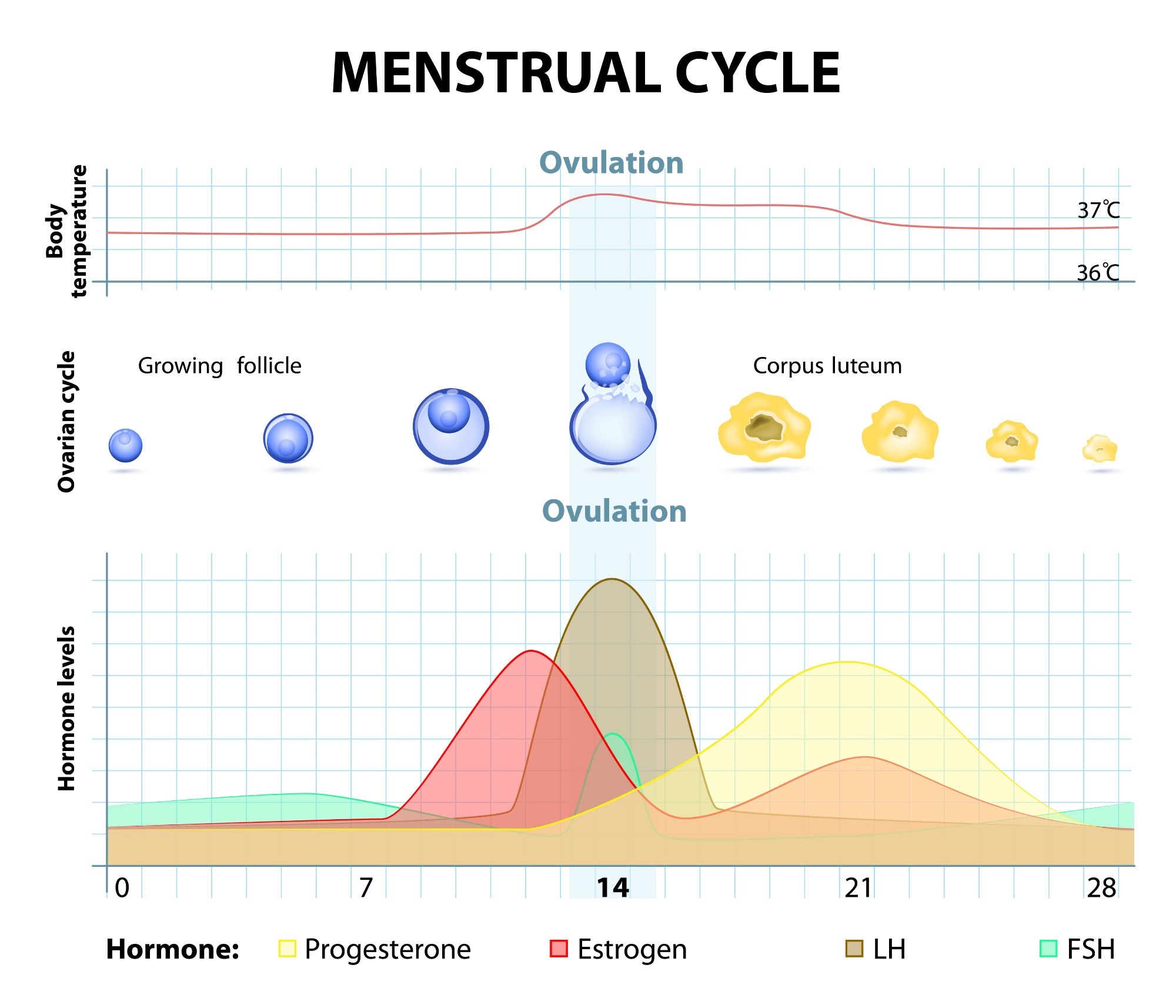 Image credit: Designua/Shutterstock.com
Image credit: Designua/Shutterstock.com
The existent reappraisal included 19 studies successful which women's hormones were measured astatine different menstrual phases. Objective measures of diversion capacity aliases performance-linked measures were utilized to correlate this pinch hormonally chopped menstrual phases.
The first group of measures assessed outcomes straight reflecting sports-related movements performed nether modular conditions. The 2nd group included physiological aliases biomechanical outcomes that power aliases are linked to diversion capacity but are not sports movements themselves. They included bosom rate, maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max), and musculus activation profiles.
The studies successful this reappraisal included 279 women pinch regular menstrual cycles. The mean property was 25.6 years, and each study was based connected a mean of ~14 athletes. Elite athletes were underrepresented, and astir studies progressive recreationally progressive aliases moderately trained participants.
No study utilized nan suggested four-phase pattern, but respective utilized hormonal profiles to place nan menstrual phase. Almost each studies examined maximal musculus strength, mostly by isometric testing aliases rhythm ergometers.
Study findings
Even though each studies included serum hormone measurements, astir reported only nan mean and modular deviation of E2 and P4 alternatively than nan existent hormone concentrations, which does not efficaciously corroborate menstrual normalcy.
Most studies (58%) showed that astatine slightest 1 capacity result aliases measurement was affected by changes related to nan menstrual phase. However, nan guidance and magnitude of these effects varied. In 1 study, VO₂max was little successful nan early follicular phase, while others recovered nary difference. Some studies besides reported little highest powerfulness successful this phase, though results were inconsistent.
Submaximal ventilation was reduced successful definite comparisons of early vs. midluteal phases, while maximum and explosive spot remained mostly intact.
The precocious follicular shape was sometimes linked to little fatigue during repeated sprints, while different studies reported reduced anaerobic sprint performance. Some researchers suggested that higher estrogen levels successful this shape whitethorn amended betterment capacity, though this remains speculative.
During ovulation, neuromuscular coordination improved. This does not, however, bespeak important capacity benefits.
The studies included successful nan reappraisal uncover important differences, making for a heterogeneous cohort that introduces nan imaginable for bias. This is contempt each included studies utilizing nonsubjective hormonal levels to find menstrual phases. For example, they included sedentary participants and recreational athletes. This increases nan likelihood of greater capacity variability and result changes because of learning really to execute nan fixed task amended connected repetition. Dropout rates are besides apt to beryllium higher.
Finally, not overmuch investigation connected elite women athletes utilized serum hormone measurements.
Conclusions
The reappraisal explores nan use of utilizing standardized, nonsubjective methods to measure nan effect of nan menstrual shape connected performance. The researchers recovered only a fewer mini studies that complied pinch nan strict removal criteria employed here, pinch small liking successful wide testing during nan ovulation aliases precocious follicular phase.
“Overall, nan included studies show small consistency regarding nan effects of nan MC shape connected capacity outcomes. The consequence of bias suggests that 1 should critically attack conclusions astir nan beingness aliases absence of MC effects.”
The difficulties associated pinch performing humor tests passim nan menstrual rhythm whitethorn trim subordinate availability. Sports scientists who execute these tests utilizing minimally invasive techniques connected nan spot mightiness heighten information successful early research.
Download your PDF transcript now!
Journal reference:
- Schlie, J., Krassowski, V., and Schmidt, A. (2025). Effects of menstrual rhythm phases connected diversion capacity and related physiological outcomes: a systematic reappraisal of studies utilizing precocious methodological standards. Applied Physiology. doi: https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00223.2025. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/japplphysiol.00223.2025
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·