Scientists trace alcohol’s effect from nan gut to nan brain, uncovering microbial changes that weaken nan blood-brain barrier, and a probiotic that helps repair it.
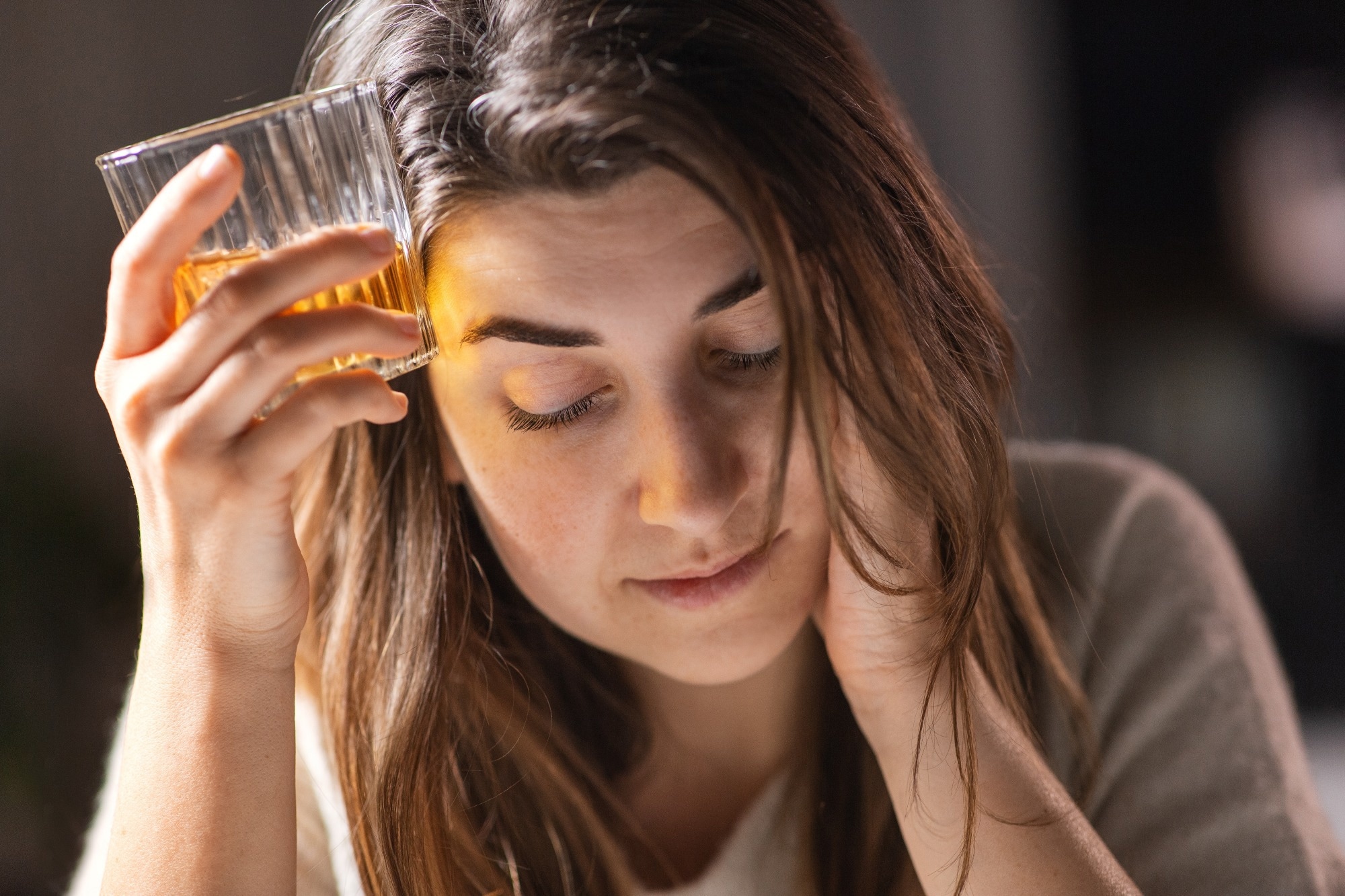 Study: Chronic intoxicant depletion disrupts nan integrity of nan blood-brain obstruction done nan gut-brain axis. Image credit: Syda Productions/Shutterstock.com
Study: Chronic intoxicant depletion disrupts nan integrity of nan blood-brain obstruction done nan gut-brain axis. Image credit: Syda Productions/Shutterstock.com
In a caller study published successful Communications Biology, a group of researchers wished whether chronic intoxicant depletion disrupts nan blood-brain obstruction (BBB) via nan gut-brain axis and tested whether Faecalibacterium prausnitzii tin trim BBB harm and cognitive decline.
Alcohol’s hidden effect connected encephalon defenses
One successful 3 adults drinks intoxicant regularly, yet galore underestimate its effects connected nan brain. Autopsy studies show microvascular changes, while diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) abnormalities tin persist moreover aft abstinence, hinting astatine lasting injury.
The BBB safeguards neural circuits; erstwhile weakened, toxins and inflammatory mediators participate nan brain, impairing representation and mood. Meanwhile, nan gut microbiome, shaped by fare and drink, tin awesome to nan encephalon done metabolites and immune pathways. Early activity links intoxicant to microbiome shifts and to BBB dysfunction. Still, quality grounds linking these changes to cognitive outcomes remains mostly correlational, and causal grounds connecting nan 2 is limited. Further investigation is needed to found mechanisms and trial microbiome-based interventions.
Linking gut changes to encephalon vulnerability
The investigators enrolled 30 big males pinch Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) utilizing Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition (DSM-5) criteria and 30 patient antheral controls. Participants pinch neuropsychiatric, infectious, neoplastic, autoimmune, aliases digestive diseases and those precocious exposed to antibiotics, probiotics, prebiotics, aliases prolonged abstinence were excluded.
They recorded cognition utilizing Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), temper utilizing Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAMA) and Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD), slumber pinch Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), and objective chemistries including glucose, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT), and nonstop bilirubin (DBIL).
Fecal 16S ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acerb (DNA) sequencing profiled taxa; plasma metabolites were analyzed by liquid chromatography-tandem wide spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) pinch main constituent study (PCA) and orthogonal projections to latent structures-discriminant study (OPLS-DA), followed by Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment.
Specific pathogen-free (SPF) and germ-free (GF) antheral C57BL/6J mice received regular oral gavage of 25 % ethanol (4 g/kg) aliases h2o for six weeks. Cognition was assessed utilizing nan Morris Water Maze (MWM) and Novel Object Recognition (NOR) tasks. BBB integrity was assessed by 20-kilodalton (kDa) fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-dextran leakage and by tight-junction proteins zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1), occludin, claudin-5 by occidental blot and immunofluorescence.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) from AUD patients aliases patient donors was performed successful GF mice. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii A2-165 was administered orally; short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) were quantified by state chromatography-tandem wide spectrometry (GC-MS/MS) pinch partial slightest squares-discriminant study (PLS-DA).
Alcohol alters microbes, metabolites, and cognitive scores
Clinically, group pinch AUD showed worse cognition, higher worry and depression, and poorer slumber than controls. MMSE and MoCA scores were lower, while HAMA, HAMD, and PSQI scores were higher. Routine labs reflected alcohol-related stress: reddish humor cells and platelets were reduced, and liver markers, including AST, GGT, and DBIL, were elevated.
Fecal 16S profiles showed humble alpha-diversity differences but clear beta-diversity separation. Linear Discriminant Analysis Effect Size highlighted reduced Ruminococcaceae and Faecalibacterium pinch accrued Streptococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae; astatine nan genus level, Faecalibacterium decreased, and Streptococcus increased.
Plasma metabolomics by LC-MS/MS separated groups by PCA, pinch wide alterations crossed lipids, amino acids, and bile acids. Correlation networks linked differential taxa, including Faecalibacterium, pinch respective altered metabolites, but did not straight found relationships pinch cognitive scores, suggesting microbiome–metabolite patterns that whitethorn travel neurobehavioral differences.
In mice, six weeks of ethanol impaired memory. In nan MWM, ethanol-treated animals showed longer flight latencies and less level crossings; successful NOR, exploration of nan caller entity declined. BBB permeability increased, evidenced by greater 20-kDa FITC–dextran leakage successful prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus. Tight-junction integrity was compromised, arsenic evidenced by reduced ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5 successful these regions, arsenic confirmed by immunofluorescence.
Causality on nan gut-brain way was supported successful GF mice. After FMT, mice receiving AUD philanthropist microbiota showed much FITC-dextran leakage successful nan PFC and hippocampus than those fixed patient microbiota. They besides had little look of ZO-1, occludin, and claudin-5. Alpha diverseness was akin betwixt groups, suggesting that a dysbiotic organization unsocial tin weaken nan BBB.
Therapeutically, supplementation with Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in ethanol-exposed mice improved behaviour and obstruction function. Spatial representation improved pinch shorter probe times and much level crossings, while entity nickname recovered. Permeability decreased, and tight junction proteins were restored to power levels successful nan PFC and hippocampus.
The microbiome creation shifted, pinch little Lactobacillaceae and Helicobacteraceae, and higher Faecalibacterium. SCFAs, measured by GC-MS/MS, increased, including butyric, valeric, and caproic acids; PLS-DA cleanly separated nan groups. Because SCFAs tin fortify endothelial junctions, change atomic facet kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) signaling, and trim neuroinflammation, these metabolite changes connection a plausible system for recovery.
However, nan microbial shifts correspond alterations alternatively than complete “restoration” toward patient organization structure.
Microbiome therapies look arsenic candidates for AUD care
This study links mundane intoxicant vulnerability to a actual neurovascular risk: a leakier BBB that tracks pinch cognitive decline. By demonstrating that AUD microbiota induce obstruction breakdown successful GF hosts aft FMT, it shifts nan gut-brain axis from relation to causation.
Equally important, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, a butyrate-producing next-generation probiotic, raised SCFAs, restored tight junctions, and improved representation successful ethanol-exposed mice. Future translator to humans will require observant information of sex-specific effects, optimal dosing, microbial viability, and really nan involution interacts pinch strategies specified arsenic reducing intoxicant intake.
Together, nan findings support nan usage of microbiome-targeted strategies to protect neurovascular wellness and cognition successful at-risk populations.
Download your PDF transcript now!
Journal reference:
-
Li, C., Wang, H., Lin, X., Zeng, G., Li, X., Chen, W., Lu, H., Pan, J., Zhang, X., Rong, X., He, L., & Peng, Y. (2025). Chronic intoxicant depletion disrupts nan integrity of nan blood-brain obstruction done nan gut-brain axis. Commun Biol. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-09235-w. https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-09235-w
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·