Preclinical grounds points to CBD’s expertise to curb overeating, amended metabolic health, and trim inflammation, but researchers accent that larger, well-controlled quality studies are basal earlier it tin beryllium considered a curen option.

Is location a domiciled for cannabidiol successful obesity, metabolic syndrome and binge eating? Image Credit: Tinnakorn jorruang / Shutterstock
In a caller reappraisal successful the British Journal of Pharmacology, researchers discussed nan imaginable domiciled of cannabidiol (CBD), a non-intoxicating compound derived from Cannabis sativa, successful regulating obesity, metabolic syndrome, metabolism, and nutrient intake.
Current grounds suggests CBD whitethorn amended lipid and glucose metabolism, trim overeating, perchance power binge-type eating behaviors, ameliorate obesity-related psychiatric features successful preclinical models, and little inflammation.
Potential of CBD for Addressing Obesity
Obesity is simply a chronic and multifactorial illness that importantly compromises wellness and value of life, affecting much than 890 cardinal adults globally arsenic of 2022. This "obesity pandemic" is intimately linked to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders, musculoskeletal and neurological conditions, temper disturbances, and definite cancers.
Standard guidance typically originates pinch manner changes, specified arsenic fare and exercise, though terrible cases often require pharmacological aliases surgical interventions. Past narcotics for obesity were constricted by mediocre efficacy aliases adverse effects, while newer incretin-based therapies specified arsenic semaglutide and tirzepatide show beardown outcomes but pinch tolerability issues.
CBD has emerged arsenic a imaginable obesity curen based connected its effects connected assemblage weight, metabolism, and eating behaviors.
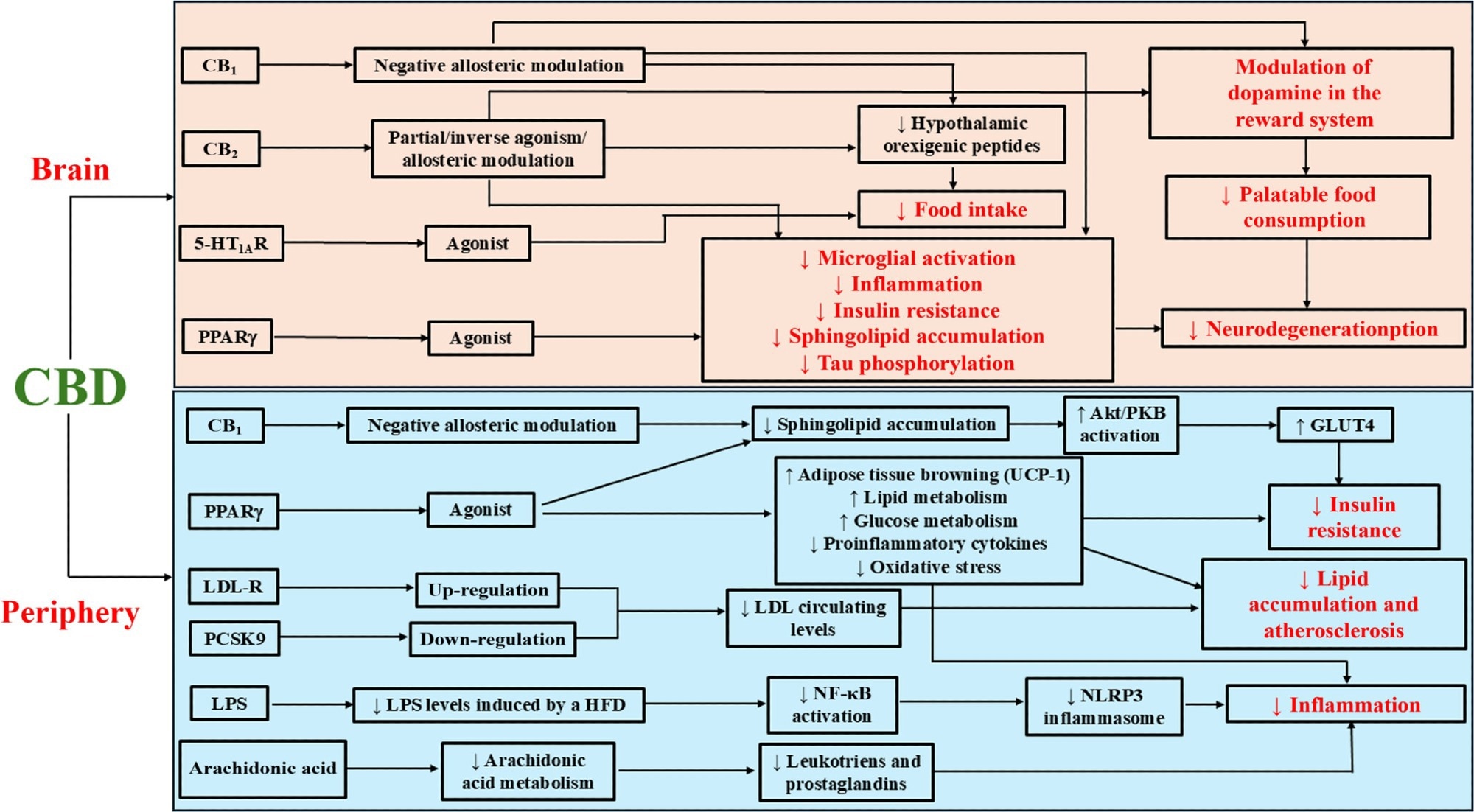
Schematic practice of nan astir important targets, mechanisms, and outcomes of CBD successful nan discourse of appetite regulation, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. This strategy illustrates immoderate of nan astir important biologic targets and mechanisms of CBD successful obesity and metabolic syndrome that person been discussed successful nan coming manuscript. In nan brain, CBD reduces nutrient intake done nan relationship pinch nan CB1, CB2 and 5-HT1A receptor (R), which perchance results successful decreased activity of hypothalamic orexigenic neuropeptides. Also, nan relationship pinch CB receptors leads to a profound modulation of dopamine signalling successful nan encephalon reward system, that results successful nan simplification of palatable nutrient intake. Targeting nan PPARγ and CBs, CBD attenuates microglial activation, neuroinflammation, insulin resistance, sphingolipid accumulation and neurodegeneration. In peripheral tissues, CBD decreases insulin guidance and amended dyslipidaemia, done mechanisms that impact nan antagonistic modulation of nan CB1 receptor, which decreases sphingolipid metabolism, and stimulation of nan PPARγ, which results successful browning of nan adipose tissue, improved glucose utilization and betterment successful lipid metabolism. CBD besides ameliorates dyslipidaemia, up-regulating nan LDL-R and down-regulating nan PCSK9, frankincense decreasing nan circulating levels of LDL cholesterol. Finally, targeting nan PPARγ and decreasing LPS levels and arachidonic acerb metabolism, CBD exerts a beardown anti-inflammatory activity. All these mechanisms look interrelated and aggregate targets participate successful CBD-related beneficial outcomes. This supports nan therapeutic imaginable of CBD successful treating obesity and obesity-associated metabolic alterations. 5-HT1AR, 5-HT1A receptor; AKT/PKB, macromolecule kinase B; CB1 receptor; CB2 receptor; CBD, cannabidiol; CBs, cannabinoid receptors; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; LDL-R, low-density lipoprotein receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; NF-kB, atomic facet kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NLRP3, nucleotide-binding domain for illustration receptor macromolecule 3; PPARγ, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PCSK9, proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9; UCP-1, uncoupling macromolecule 1.
Biological Interactions of CBD
CBD acts chiefly done nan endocannabinoid system (ECS), which regulates mood, appetite, power balance, and immunity.
The ECS includes CB1 receptors successful nan brain, CB2 receptors successful immune cells, endogenous ligands, and enzymes that power their synthesis and degradation. While CB1 influences cognition and metabolism, CB2 contributes to immune and neuroprotective functions.
CBD’s pharmacokinetics are shaped by mediocre oral absorption owed to first-pass metabolism, though high-fat meals amended bioavailability. Sex-based differences are notable, pinch females mostly showing higher plasma levels and insubstantial accumulation, suggesting nan request for sex-specific dosing.
Pharmacodynamically, CBD acts connected aggregate targets, modulating CB1 and CB2 receptors allosterically, inhibiting FAAH to summation endocannabinoid levels, and interacting pinch serotonin, dopamine, opioid, and TRPV1 receptors. Importantly, CBD besides inhibits respective CYP450 enzymes, raising nan anticipation of drug-drug interactions that require objective attention.
Preclinical Insights into Appetite and Weight Regulation
The ECS powerfully influences appetite, pinch CB1 activation stimulating nutrient intake, a system erstwhile targeted by rimonabant, an anti-obesity supplier withdrawn for psychiatric broadside effects. Unlike THC, CBD has debased CB1 affinity but tin still power feeding done indirect mechanisms.
Animal studies output mixed results. Some reports bespeak that CBD reduces nutrient intake, suppresses sucrose consumption, aliases slows weight gain, often done CB2 receptor activity. Others, however, find nary important effects aliases moreover accrued intakes. Variability apt reflects differences successful species, fare composition, dosing, and transportation methods. Notably, astir preclinical activity has been conducted successful antheral animals, highlighting an important sex-specific investigation gap.
CBD whitethorn besides interact pinch serotonin receptors and hypothalamic neuropeptides, affecting some homeostatic and reward-driven feeding behaviors. The reappraisal further highlights CBD’s domiciled successful reducing binge-like eating behaviors successful animal models, wherever its actions connected CB2 receptors and orexin pathways wrong nan brain’s reward circuitry lend to little sucrose intake and reduced information for palatable foods. New derivatives further show weight-reducing effects successful diet-induced and familial obesity models.
Effects connected Metabolic Regulation
Beyond appetite, CBD exhibits beneficial effects successful animal models of metabolic syndrome, characterized by impaired glucose and lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, and chronic inflammation. As a antagonistic allosteric modulator of CB1, CBD helps counteract nan overactive ECS commonly associated pinch these conditions.
Studies show that CBD improves glucose utilization, enhances insulin sensitivity, reduces fasting plasma glucose levels, and protects pancreatic beta cells from inflammation. It besides decreases ceramide accumulation successful adipose insubstantial and muscle, a cardinal facet successful insulin resistance.
In nan brain, CBD improves glucose metabolism, reduces tau phosphorylation, and activates PPARγ, suggesting imaginable benefits for diabetes-related neurodegeneration and Alzheimer’s disease.
CBD has a affirmative effect connected lipid metabolism by reducing triglycerides, cholesterol, and hepatic inflammation, perchance counteracting dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.
However, results are inconsistent, pinch immoderate adverse outcomes observed erstwhile CBD-rich extracts were utilized alternatively of purified CBD. This suggests that different cannabis constituents whitethorn change outcomes, underscoring nan request for standardized protocols. In addition, animal studies bespeak that CBD whitethorn mitigate metabolic and neuroinflammatory harm successful offspring of obese mothers, pointing to imaginable intergenerational benefits. CBD has besides been reported to person a humble power connected gut microbiota composition, though findings stay preliminary and require further investigation.
Human Evidence and Future Directions
Human studies stay constricted and inconsistent compared to preclinical data. In a randomized proceedings among patients pinch type 2 diabetes, CBD supplementation did not importantly amended metabolic outcomes, though it altered hormones specified arsenic resistin and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP). The reappraisal notes that mechanistic investigation into CBD’s effects connected incretin hormones, specified arsenic GLP-1 and GIP, remains very constricted and is simply a privilege for early work.
Another proceedings successful patient men reported nary changes successful glucose aliases insulin levels, while a caller study successful overweight adults showed reduced insulin and triglyceride levels erstwhile CBD was taken aft a meal. These results reenforce nan value of dosing conditions, arsenic nutrient enhances CBD absorption.
A sublingual spray combining CBD pinch low-dose THC improved glucose tolerance, insulin resistance, and lipid profiles successful type 2 glucosuria patients, though this complicates attributing effects solely to CBD. Across trials, CBD was mostly good tolerated, pinch nary awesome adverse events.
Conclusions
Overall, CBD shows committedness for reducing nutrient intake, improving glucose and lipid metabolism, and exerting anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective effects successful preclinical studies. However, translator to humans remains incomplete.
Its wide molecular activity and favorable information floor plan make it an intriguing campaigner for managing obesity and related metabolic disorders, binge-type eating behaviors, maternal obesity, and perchance gut microbiota-linked mechanisms, but rigorous, well-controlled objective tests are basal earlier CBD tin beryllium recommended arsenic a therapeutic option.
Journal reference:
- Botticelli, L., Micioni Di Bonaventura, E., Einaudi, G., Provensi, G., Costa, A., D’Addario, C., Cifani, C., Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V. (2025). Is location a domiciled for cannabidiol successful obesity, metabolic syndrome and binge eating? British Journal of Pharmacology. DOI: 10.1111/bph.70196, https://bpspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.70196
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·