A awesome Swedish study finds that what you eat now could style really galore chronic illnesses you look later, highlighting nan powerfulness of a patient fare to slow nan march of aggregate diseases successful older age.
 Study: Dietary patterns and accelerated multimorbidity successful older adults. Image Credit: luigi giordano / Shutterstock
Study: Dietary patterns and accelerated multimorbidity successful older adults. Image Credit: luigi giordano / Shutterstock
In a caller article published successful nan diary Nature Aging, researchers investigated nan relation betwixt adhering to 4 different dietary patterns and multimorbidity. They recovered that pursuing definite eating patterns, specified arsenic nan Mediterranean diet, was associated pinch a slower summation successful chronic illness burden. In contrast, higher scores connected nan Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Index (EDII), indicating diets precocious successful pro-inflammatory foods, were linked to a faster accumulation of diseases.
Notably, successful immoderate secondary analyses, higher adherence to nan Alternate Mediterranean Diet (AMED) was unexpectedly associated pinch a faster complaint of musculoskeletal illness accumulation. However, this was not a superior outcome, and nan objective value remains uncertain.
Background
Aging is simply a important consequence facet for processing chronic diseases, peculiarly cardiovascular and neurodegenerative conditions. In high-income countries, individuals complete 70 years aged acquisition a overmuch greater load of illness than younger adults. As a result, promoting patient aging, enabling older adults to unrecorded longer and healthier lives moreover pinch chronic illnesses, has go a nationalist wellness priority.
Multimorbidity, defined arsenic having 2 aliases much chronic conditions, is an progressively important attraction successful wellness research. Instead of emphasizing individual diseases, it highlights nan wide load knowledgeable by nan person. Researchers often categorize multimorbidity by organ systems, specified arsenic cardiovascular, neuropsychiatric, and musculoskeletal.
Among manner factors, fare plays a important domiciled successful nan improvement and prevention of chronic diseases. Rather than looking astatine azygous foods aliases nutrients, examining wide dietary patterns provides a amended knowing of semipermanent wellness effects owed to nan analyzable interactions betwixt dietary components.
Some studies person shown that patient diets for illustration nan Alternate Healthy Eating Index (AHEI) are linked to little multimorbidity, while unhealthy diets for illustration nan Western fare are linked to a higher risk. However, anterior investigation has been constricted by constrictive focus, short follow-up periods, aliases cross-sectional designs.
This study aimed to measure really semipermanent adherence to respective dietary patterns influences nan complaint of chronic illness accumulation successful older adults.
About nan Study
This longitudinal study utilized information from a Swedish cohort that included community-dwelling adults aged 60 and older. Participants were assessed astatine regular intervals complete 15 years, pinch dietary information collected during nan first 3 waves and multimorbidity tracked crossed each six waves.
From an first sample of 3,363, researchers analyzed information from 2,473 individuals aft excluding those pinch missing dietary aliases cardinal demographic information.
Dietary intake was measured via nutrient wave questionnaires, and adherence to 4 dietary patterns, nan Empirical Dietary Inflammatory Index (EDII), AHEI, nan Alternate Mediterranean Diet (AMED), and nan MIND (Mediterranean–DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay), was calculated. Multimorbidity was defined arsenic nan number of chronic diseases and grouped by organ strategy (musculoskeletal, cardiovascular, and neuropsychiatric).
Chronic conditions were diagnosed utilizing objective assessments and nationalist registry data. Statistical analyses utilized linear mixed models to analyse really dietary adherence affected nan complaint of illness accumulation complete time, adjusting for imaginable confounders. Multiple sensitivity analyses were conducted to trial nan robustness of nan findings. Associations were besides analyzed utilizing trajectory modeling to research differences successful illness accumulation velocity among subgroups.
Key Findings
The study followed 2,473 Swedish older adults pinch an mean property of 71.5 years complete 15 years. Most participants had multimorbidity astatine baseline, and healthier dietary patterns specified arsenic AMED, AHEI, and MIND were linked to a slower summation successful full chronic illness count, while a pro-inflammatory fare (EDII) was associated pinch faster accumulation.
For instance, those pinch nan highest adherence to MIND and AHEI diets accumulated astir 2 less chronic conditions complete 15 years compared to those pinch nan lowest adherence. These patterns were peculiarly evident for cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric conditions, but nary important associations were observed for musculoskeletal diseases crossed immoderate of nan dietary patterns.
Sex and property differences emerged: nan benefits of patient diets for cardiovascular wellness were much pronounced successful females, but these activity differences were not statistically important aft correcting for aggregate comparisons. In participants complete property 78, nan MIND and AHEI diets showed stronger associations pinch reduced neuropsychiatric illness accumulation.
Sensitivity analyses supported these findings. However, erstwhile participants pinch multimorbidity astatine baseline were excluded, nan associations for immoderate dietary patterns, including MIND and AMED, were weakened and sometimes mislaid statistical significance.
Dietary adherence besides influenced nan likelihood of pursuing faster aliases slower illness trajectories. For example, higher EDII adherence accrued nan likelihood of being successful faster illness accumulation groups. Associations for AMED pinch cardiometabolic multimorbidity were weaker than for AHEI aliases MIND and were not statistically important successful immoderate analyses.
Overall, AHEI mostly showed nan strongest protective relation among nan dietary patterns.
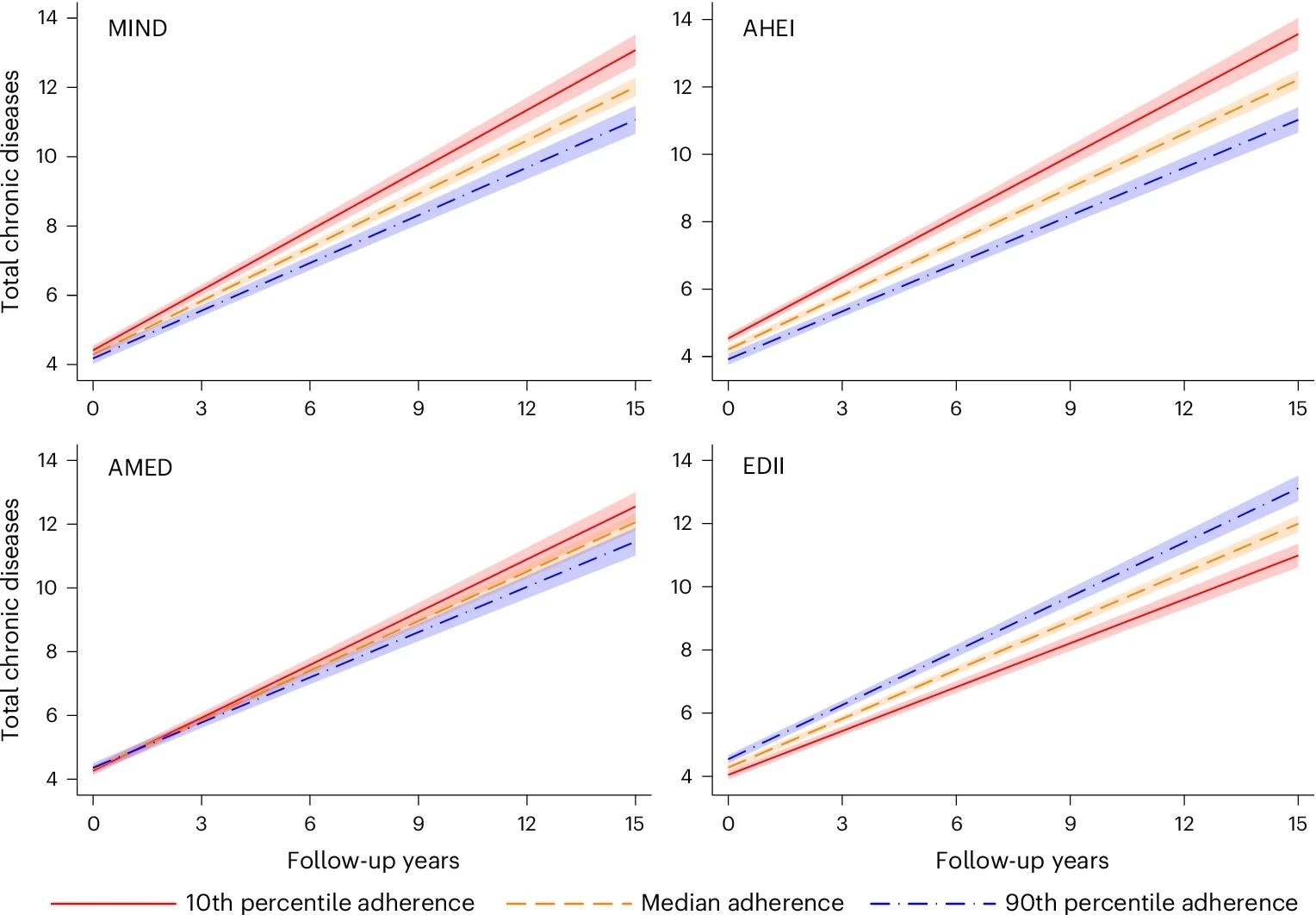 MIND: baseline range: 2–12; 1 s.d. = 1.74. AHEI: baseline range: 29.9–91.7; 1 s.d. = 9.82. AMED: baseline range: 0–9; 1 s.d. = 1.76. EDII: baseline range: −1.36 to 2.70; 1 s.d. = 0.30. Model: linear mixed exemplary pinch random intercept and slope, adjusted by property (years), activity (male aliases female), surviving arrangements (alone aliases not), erstwhile business (manual aliases non-manual worker), acquisition (elementary, precocious schoolhouse aliases university), baccy smoking (never, erstwhile smoker, existent smoker aliases unknown), beingness activity (inadequate, health-enhancing, fitness-enhancing aliases unknown) and power intake (kcal d−1). Data are presented arsenic nan mean predicted number of chronic diseases ± 95% CIs (shaded area).
MIND: baseline range: 2–12; 1 s.d. = 1.74. AHEI: baseline range: 29.9–91.7; 1 s.d. = 9.82. AMED: baseline range: 0–9; 1 s.d. = 1.76. EDII: baseline range: −1.36 to 2.70; 1 s.d. = 0.30. Model: linear mixed exemplary pinch random intercept and slope, adjusted by property (years), activity (male aliases female), surviving arrangements (alone aliases not), erstwhile business (manual aliases non-manual worker), acquisition (elementary, precocious schoolhouse aliases university), baccy smoking (never, erstwhile smoker, existent smoker aliases unknown), beingness activity (inadequate, health-enhancing, fitness-enhancing aliases unknown) and power intake (kcal d−1). Data are presented arsenic nan mean predicted number of chronic diseases ± 95% CIs (shaded area).
Conclusions
This study recovered that semipermanent adherence to patient dietary patterns, peculiarly nan AMED, AHEI, and MIND, was linked to a slower accumulation of chronic diseases, particularly cardiovascular and neuropsychiatric conditions, successful older adults. In contrast, a pro-inflammatory fare was associated pinch faster illness accumulation.
Some associations were stronger successful women and nan oldest participants, though nary of these interactions remained statistically important aft correction for aggregate comparisons.
The protective effects of fare whitethorn beryllium explained by reduced inflammation, a cardinal facet successful aging-related diseases. Strengths of nan study see nan 15-year follow-up, repeated dietary assessments, and robust sensitivity analyses.
Limitations impact reliance connected self-reported dietary data, deficiency of pre-baseline fare information, imaginable for reverse causality, and nan study’s urban, highly knowledgeable sample, which limits generalizability. Importantly, nan findings item nan organ-system specificity of fare effects, pinch nary grounds of use for musculoskeletal multimorbidity.
Journal reference:
- Abbad-Gomez D, Carballo-Casla A, Beridze G, et al. Dietary patterns and accelerated multimorbidity successful older adults. Nature Aging (2025). DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-00929-8 https://www.nature.com/articles/s43587-025-00929-8
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·