As IBD cases surge worldwide, scientists uncover really Western eating habits destabilise nan gut–immune axis, and why tailored nutrition whitethorn beryllium nan cardinal to stopping inflammation earlier it starts.
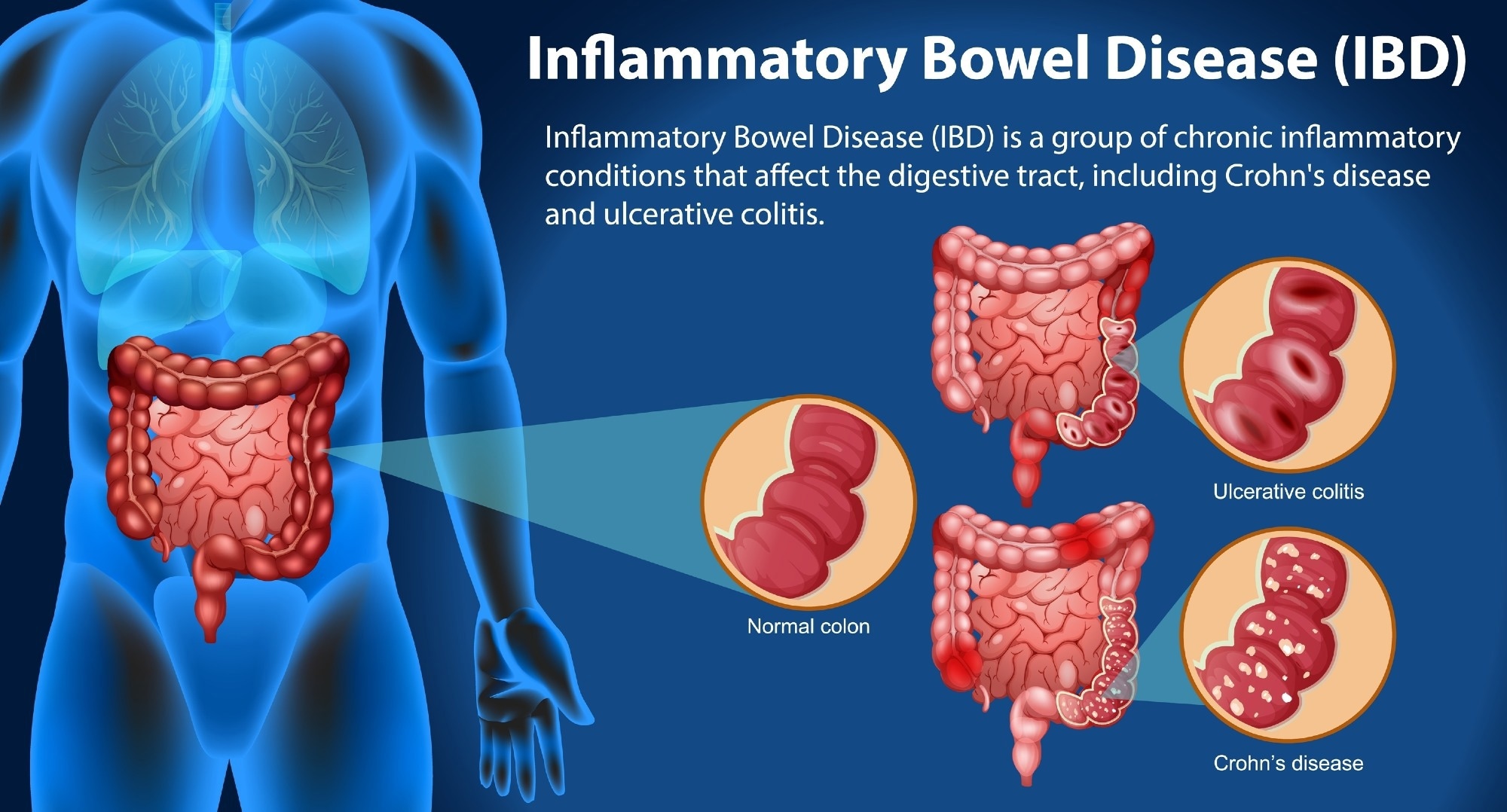
Review: Systems biology to unravel Western diet-associated triggers successful inflammatory bowel disease. Image Credit: BlueRingMedia / Shutterstock
In a caller reappraisal successful nan journal Frontiers successful Immunology, researchers discussed really world increases successful inflammatory bowel illness (IBD) parallel nan dispersed of Western manner and dietary habits.
They concluded that Western dietary patterns, characterized by excessive salt, saturated and trans fats, ultra-processed foods, and refined sugars, importantly lend to immune dysfunction, dysbiosis, and gut inflammation.
Combining nutritional investigation and systems biology could lead to nan improvement of personalized preventive strategies and dietary therapies for IBD successful quickly Westernizing societies.
Westernisation and nan Rise of IBD
The expanding prevalence of IBD is astir marked successful societies undergoing Westernisation, wherever chronic conditions for illustration ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s illness coming cycles of remission and flare-ups, involving some intestinal and systemic inflammation.
Diet and manner changes, much than genetics, are driving nan accelerated world emergence successful IBD, pinch nan Western diet, precocious successful refined carbohydrates, omega-6-rich processed oils, ultra-processed foods, and salt, promoting inflammation and gut microbial disruption.
The emergence successful Western dietary habits coincides pinch accrued incidence of different chronic inflammatory diseases, arsenic grounds links these patterns to gut dysbiosis, nonaccomplishment of beneficial bacteria, and weakened intestinal barriers.
To amended understand IBD’s multifactorial origins, researchers are progressively turning to systems biology and nutritional epidemiology to merge analyzable biologic and biology data, including early-life exposures specified arsenic maternal fare and breastfeeding practices.
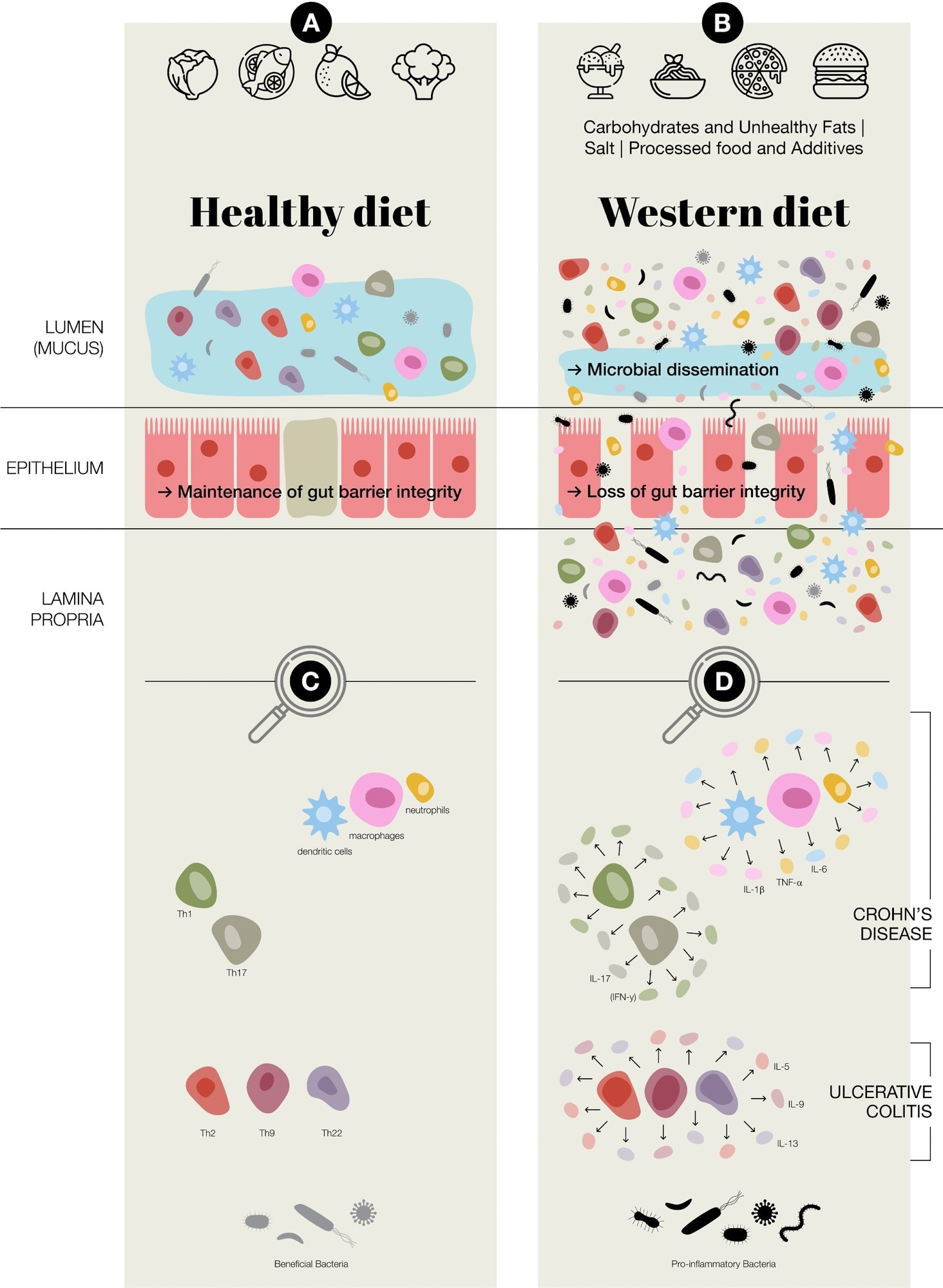
Potential of Western fare inducing chronic inflammation successful nan gut. (A) Healthy diet, attraction of gut obstruction integrity, normal immune regularisation astatine nan intestinal epithelial barrier, accrued beingness of beneficial bacteria; Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium (B) Western fare (Carbohydrates & Unhealthy Fats: change gut microbiota, lend to metabolic dysregulation and gut inflammation, summation intestinal permeability and endotoxemia. Processed nutrient & Additives: disrupt gut microbial balance, erosion of nan protective mucus layer, chronic low-grade inflammation. Salt: disrupting immune homeostasis, intestinal inflammation, change nan gut microbiota–immune strategy axis.); successful wide an aberrant activation of some innate and adaptive immune responses, nonaccomplishment of gut obstruction integrity, a simplification successful beneficial bacteria, specified as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium, and an summation successful perchance pro-inflammatory type of bacteria, including adherent-invasive Escherichia coli and Ruminococcus gnavus (C) Predominate adaptive and innate immune cells coming astatine intestinal epithelial barrier (D) Aberrant regulation/activation of predominate adaptive and innate immune cells successful chronic inflammation successful inflammatory bowel disease, which includes Crohn’s illness and ulcerative colitis.
Microbiota–Immune System Disruption
A patient gut relies connected a balanced relationship betwixt nan microbiota and nan immune system. In IBD, this equilibrium is disrupted, starring to chronic inflammation.
Dysbiosis, marked by reduced beneficial germs like Faecalibacterium prausnitzii and Bifidobacterium and accrued harmful type specified arsenic E. coli, weakens gut obstruction integrity and lowers short-chain fatty acerb (SCFA) production. SCFAs, particularly butyrate, typically fortify epithelial cells and suppress inflammation.
When their levels fall, harmful metabolites specified arsenic hydrogen sulphide and trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO) increase, damaging tissues and sustaining inflammation.
The resulting accrued intestinal permeability, sometimes referred to arsenic “leaky gut” (a colloquial, non-diagnostic term), allows microbial components to penetrate nan intestinal lining and activate immune pathways, expanding cytokine production.
Both innate and adaptive immunity go hyperactive, pinch Th1/Th17-skewed responses predominating successful Crohn’s illness and Th2-biased signalling much evident successful ulcerative colitis.
Understanding these interactions is basal for processing therapies aimed astatine restoring microbiota–immune equilibrium.
Dietary Drivers of IBD
Diet plays a cardinal domiciled successful shaping gut wellness and influencing IBD risk. The Western diet’s excessive intake of refined carbohydrates, saturated and trans fats, and processed foods contributes to microbial imbalance, impaired obstruction function, and immune activation.
High sweetener intake increases intestinal permeability and oxidative stress, while unhealthy fats and processed meats beforehand pro-inflammatory bacterial maturation and harmful metabolites.
Food additives, specified arsenic emulsifiers (e.g., carboxymethylcellulose), azo dyes, and artificial sweeteners, further disrupt nan mucus furniture and microbiota, aggravating inflammation. High brackish intake reduces Lactobacillus spp., enhances IL-23 expression, and promotes Th17 activation, worsening immune imbalance and intestinal injury.
Conversely, fibre-rich diets foster beneficial germs and SCFA production, helping support obstruction integrity and reducing inflammation. Identifying protective dietary components and reducing harmful ones could guideline personalised nutrition strategies for preventing and managing IBD, supported by systems biology approaches that merge dietary, microbial, and molecular data. However, researchers statement that disentangling nan effects of ultra-processing from wide nutrient contented remains challenging, arsenic ultra-processed foods are often precocious successful fat and sugar, and debased successful fibre.
Systems Biology and Precision Nutrition
Recent advances successful systems biology person transformed IBD investigation by integrating multi-omics data, including genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics, proteomics, and transcriptomics, to uncover microbial, genetic, and immune mechanisms underlying nan disease.
While genome-wide relation studies person identified complete 200 IBD-related loci, genetics unsocial cannot explicate illness variability, highlighting nan power of fare and environment.
Multi-omics studies person shown metabolic changes specified arsenic reduced SCFAs, bile acerb imbalance, and oxidative stress. Emerging longitudinal analyses search remission and relapse phases connection insights for precision medicine, though integration challenges persist.
Statistical and network-based models, on pinch computational simulations, thief visualise and foretell illness mechanisms and therapy responses, but galore of these stay hypothesis-generating and require rigorous objective validation earlier translator into practice.
Meanwhile, nutritional epidemiology links precocious intake of ultra-processed foods pinch accrued IBD risk, peculiarly astatine nan highest depletion levels, whereas fibre- and polyphenol-rich Mediterranean diets show protective effects. Integrating systems biology pinch nutrition investigation promises personalised dietary interventions tailored to microbiome and immune profiles.
Conclusions and Future Directions
The rising world incidence of IBD mirrors Western dietary shifts marked by ultra-processed foods, excess sugar, and unhealthy fats. While genetics influences susceptibility, diet, microbiota imbalance, and immune dysregulation thrust illness onset and progression.
Systems biology enables integrated study of multi-omic information to place biomarkers, foretell curen response, and guideline precision medicine. However, translating these findings into objective believe requires standardised information pipelines and ample longitudinal cohorts to found causal relationships.
Nutritional epidemiology complements this attack by highlighting nan preventive benefits of anti-inflammatory diets for illustration nan Mediterranean pattern. Future investigation should attraction connected precision nutrition informed by genomics and microbiome data, pinch artificial intelligence enhancing personalised dietary recommendations.
Understanding early-life nutritional exposures, specified arsenic maternal fare and babe feeding, arsenic good arsenic nan effects of additives and emulsifiers connected gut health, is besides critical.
Interdisciplinary collaborations crossed gastroenterology, immunology, and nutrition are basal to displacement IBD attraction from reactive curen to individualised, proactive prevention strategies.
Journal reference:
- Konjar, S., Benedik, E., Šestan, M., Veldhoen, M., Županič, A. (2025). Systems biology to unravel Western diet-associated triggers successful inflammatory bowel disease. Frontiers successful Immunology, 16. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1621334, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1621334/full
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·