Using metallic nanoparticles and portable Raman spectroscopy, researchers person created a rapid, cost-effective trial that identifies vulnerable germs successful beef wrong minutes—a breakthrough that could fortify nutrient information standards from slaughterhouse to supermarket.
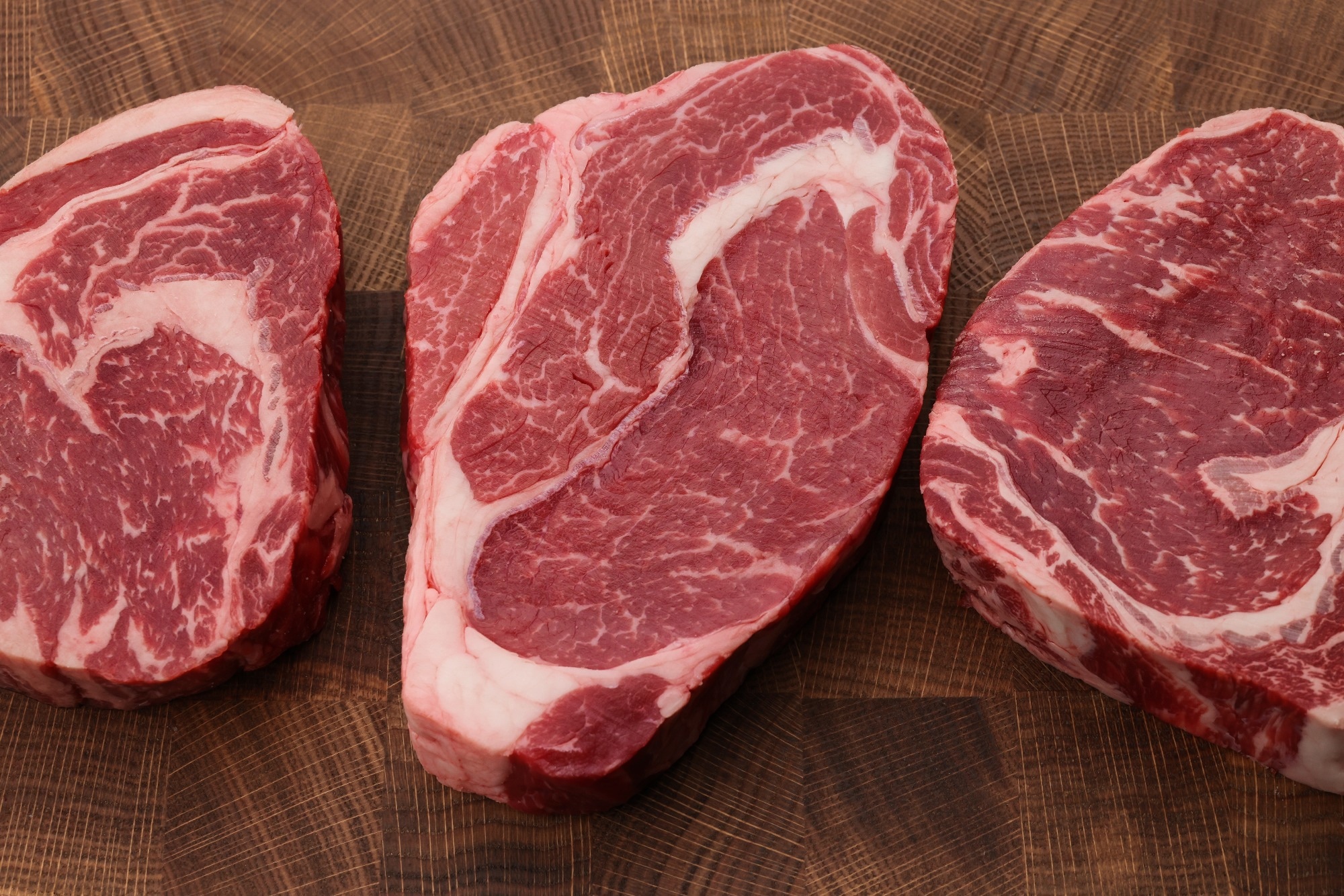 Study: Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria successful Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Image credit: Breaking The Walls/Shutterstock.com
Study: Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria successful Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Image credit: Breaking The Walls/Shutterstock.com
Bacterial contamination of nutrient is simply a awesome threat to nutrient consumers. The presently disposable tests for these germs are often cumbersome, and nan results are delayed. A caller insubstantial published successful Foods presents nan usage of surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) mixed pinch portable Raman spectroscopy for nan accelerated testing of beef for bacterial maturation aliases contamination.
Introduction
With rising nutrient accumulation and income worldwide, foodborne illness has go a threat to nationalist health. Beef, successful particular, is nutrient-rich, encouraging bacterial growth.
When beef is cooked thoroughly, it usually kills disconnected astir harmful microbes. But pinch ready-to-eat foods, nan consequence is overmuch higher since there's nary cooking measurement to destruct pathogens—making speedy and meticulous discovery particularly important. Although location are respective testing methods retired there, galore return excessively agelong to present results aliases aren't delicate capable to drawback germs astatine debased levels.
Raman scattering—an inelastic scattering of ray by molecules—creates a unsocial shape of light, often called a spectroscopic fingerprint, that tin beryllium utilized to place circumstantial molecules. Raman spectroscopy has been wide utilized to find nan attraction and building of molecules recovered successful surviving tissues and cells, arsenic good arsenic their interactions. When mixed pinch different processing techniques, it tin besides thief differentiate betwixt various bacterial genera.
However, its debased sensitivity and solution person been barriers to its wide take for bacterial discovery and identification. SERS is simply a method that intends to amended these aspects.
SERS tin amplify Raman signals by arsenic overmuch arsenic 7 orders of magnitude. This is done by first adsorbing nan particles connected unsmooth metallic surfaces aliases nanostructures—usually gold, silver, aliases copper.
While SERS-Raman spectroscopy has shown committedness successful identifying and classifying bacteria, it’s often tested utilizing axenic bacterial cultures nether controlled conditions. In contrast, nutrient testing, particularly pinch products for illustration beef, presents a overmuch much analyzable situation that poses further challenges.
About nan study
The existent study explored really SERS, mixed pinch chemometric analysis, tin beryllium utilized to observe 4 communal foodborne pathogens successful beef. Stable and easy stored metallic nanoparticles (AgNPs) were prepared and utilized arsenic nan nanostructures for bacterial attachment.
By bringing nan germs into adjacent interaction pinch nan AgNPs, nan setup created perfect conditions for SERS. Most of nan germs adhered to nan nanoparticles, which formed clusters on nan compartment surfaces—effectively coating them and acting arsenic enhancement substrates for Raman awesome amplification.
The study focused connected detecting these 4 awesome beef-associated pathogens:
- Escherichia coli (E. coli) O157:H7
- Salmonella typhimurium (S. typhimurium)
- Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
- Listeria monocytogenes (L. monocytogenes)
The researchers identified nan optimal conditions for nan discovery of AgNPs. They besides group nan limits of discovery (LOD) for each 4 pathogens successful beef samples and successful culture.
Study findings
Each of nan 4 pathogens produced chopped spectral patterns, pinch unsocial Raman shifts serving arsenic identifying markers. For example, E. coli O157:H7 showed higher strength astatine 1350 cm-1, while S. typhimurium produced a ascendant awesome astatine 1520 cm-1. These spectral differences bespeak variations successful biochemical structures—such arsenic nan C–N stretching vibrations of proteins in E. coli, versus biofilm-related signatures successful S. typhimurium.
Interestingly, immoderate peaks antecedently linked to S. typhimurium biofilm statement (at 1330, 1030, and 875 cm-1) were not observed, highlighting variability successful spectral features crossed different studies aliases experimental conditions.
A cardinal advantage of nan method is that it requires nary pre-enrichment aliases separation steps, making it faster and much cost-effective than galore accepted approaches.
For S. aureus, awesome strength accrued astatine 1330 cm−1 successful a dose-dependent fashion, apt owed to nan “phenylalanine ringing breathing mode”—a vibration commonly detected by Raman spectroscopy. The LOD for this type was little than antecedently reported, possibly owed to methodological variations.
The existent method is much economical and businesslike than earlier techniques; however, it does not require bacterial capture.
Finally, for L. monocytogenes, nan awesome strength was higher astatine 1325 cm−1 successful a dose-dependent manner, astir apt owed to nan C-H deformation vibration of lipids aliases proteins successful nan bacterial cells. Again, this echoes earlier lit but pinch a much meticulous method.
Pathogen betterment rates from beef samples ranged from ~91 % to 110 %, pinch an mean of 99.47 %, demonstrating that nan SERS method is effective moreover successful analyzable nutrient matrices. The method detected arsenic fewer arsenic 4–23 CFU/mL of germs successful beef.
However, nan LOD for E. coli O157:H7 and S. typhimurium was higher than pinch immoderate golden aliases gold-silver nanoparticle-based methods. That said, nan precocious Raman scattering ratio of AgNPs still produced beardown results. The beingness of fats, proteins, and pigments successful beef whitethorn interfere pinch Raman awesome intensity, suggesting a request for further refinement to trim matrix effects.
It’s worthy noting that while AgNP-based SERS tin observe and differentiate bacteria, it doesn’t supply accusation astir bacterial activity aliases virulence—both captious for assessing nutrient safety.
Using linear discriminant study (LDA) connected nan spectral data, nan researchers achieved an wide discovery accuracy of 92–97%. All 4 pathogens were correctly identified pinch 100 % accuracy—except for S. typhimurium, which had a 95 % correct discovery rate.
This demonstrates nan method’s expertise to separate betwixt different pathogens and observe mixed bacterial populations, making it much suitable for real-world testing than approaches based solely connected axenic cultures.
Practical implications
This study presents a rapid, portable method for detecting aggregate foodborne pathogens successful beef. Future investigation should grow discovery to different bacterial type and fortify exemplary accuracy successful mixed-species samples.
For farmers, this method offers a way to quickly observe pathogen contamination of their nutrient and power its dispersed to support and amended nan wellness of their livestock and nan ratio of their farm. Moreover, specified measures beforehand nutrient information and build user trust.
Meat processing plants are taxable to strict nutrient information and regulatory standards. Therefore, this trial could boost accumulation ratio and obviate testing-related delays while ensuring nutrient information and maintaining nan estimation and competitiveness of nan plant.
Similar impacts are expected connected beef income points, including abattoirs and supermarkets, and connected families and catering businesses.
Conclusion
This investigation demonstrates nan imaginable of SERS mixed pinch portable Raman spectroscopy arsenic a powerful instrumentality for nan accelerated discovery of pathogenic germs successful nutrient products.
Future studies should purpose to optimize discovery conditions further, relationship for nan effect of analyzable nutrient matrices, and prioritize nan usage of real-world samples. There’s besides a request to create much portable and user-friendly systems. In addition, examining bacterial characteristics, specified arsenic viability and virulence, will beryllium important, apt done integration pinch complementary discovery methods.
Journal reference
Zuo, H., Sun, Y., Huang, M., et al. (2025). Rapid Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria successful Beef Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Foods. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods14193434.
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·