As scientists uncover really age-altered antibodies ignite inflammation and insubstantial decline, a caller era of immune-based anti-aging therapies is opening to emerge.
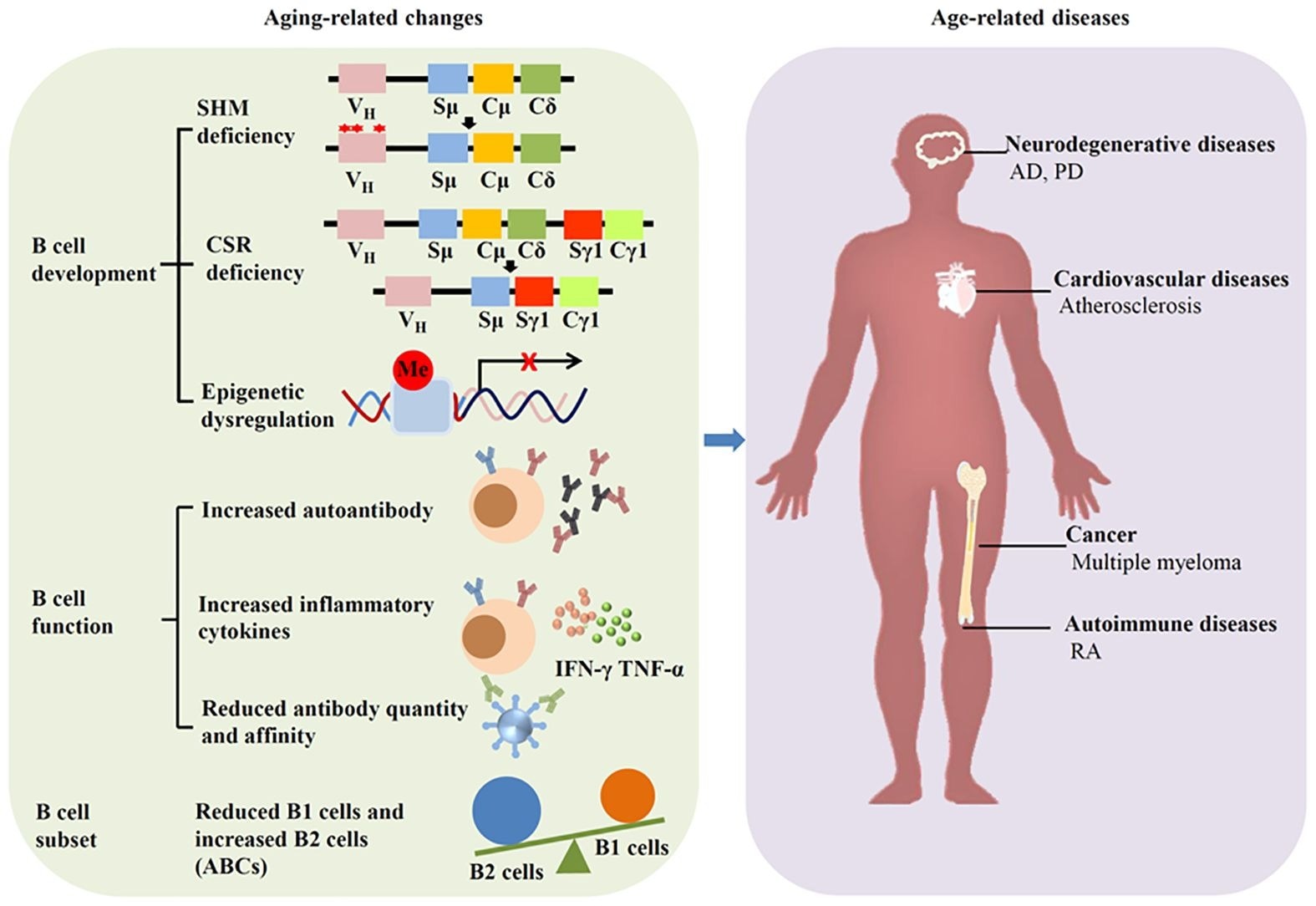
Aging affects B cells and induces diseases. Aging tin change nan development, usability and subset of B cells, starring to age-related diseases specified arsenic neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
In a caller reappraisal published successful nan journal Frontiers successful Immunology, researchers summarized lit connected immunoglobulin changes linked to aging and related diseases.
Aging is 1 of nan starring causes of chronic diseases, specified arsenic cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and cardiovascular diseases, which yet will lead to death. Among nan various factors contributing to aging, cellular senescence is regarded arsenic a hallmark and driver of insubstantial dysfunction. Senescent cells accumulate successful organs and tissues during aging, and their clearance tin mitigate aging and related diseases. Studies person reported immunoglobulin accumulation adjacent to senescent cells.
Reports besides bespeak accrued look of immunoglobulin-related genes successful aged tissues, suggesting that IgG accumulation has been projected arsenic a hallmark of quality aging, partially owed to its expertise to trigger cellular senescence and chronic inflammation. Age-related changes successful IgG glycosylation, specified arsenic reduced galactosylation and sialylation, further heighten pro-inflammatory signaling and lend to inflammaging done nan REST/NF-κB pathway. Gaining insights into nan mechanisms underlying aging tin amended nan value of life and lifespan. In nan coming study, researchers reviewed nan lit connected immunoglobulin changes associated pinch aging and related diseases.
Aging and B cells
Aging leads to important changes successful nan immune system, chiefly successful nan humoral compartment mediated by B cells. This phenomenon, immunosenescence, tin elevate nan severity and wave of infectious diseases and alteration responses to vaccination. Human and murine bony marrow show diminished B compartment precursors during aging, attributable to microenvironmental changes associated pinch age.
Moreover, B1 cells, which are fetal liver-derived, alteration pinch aging successful older individuals, on pinch a simplification successful nan usability and number of earthy antibodies. B2 cells (conventional B cells) grounds functional impairments associated pinch aging, which manifest arsenic defective isotype switching successful aged cells. Although peripheral B2 cells stay unchanged successful aged mice, follicular and marginal area B2 cells alteration pinch age, accompanied by an summation successful autoantibodies.
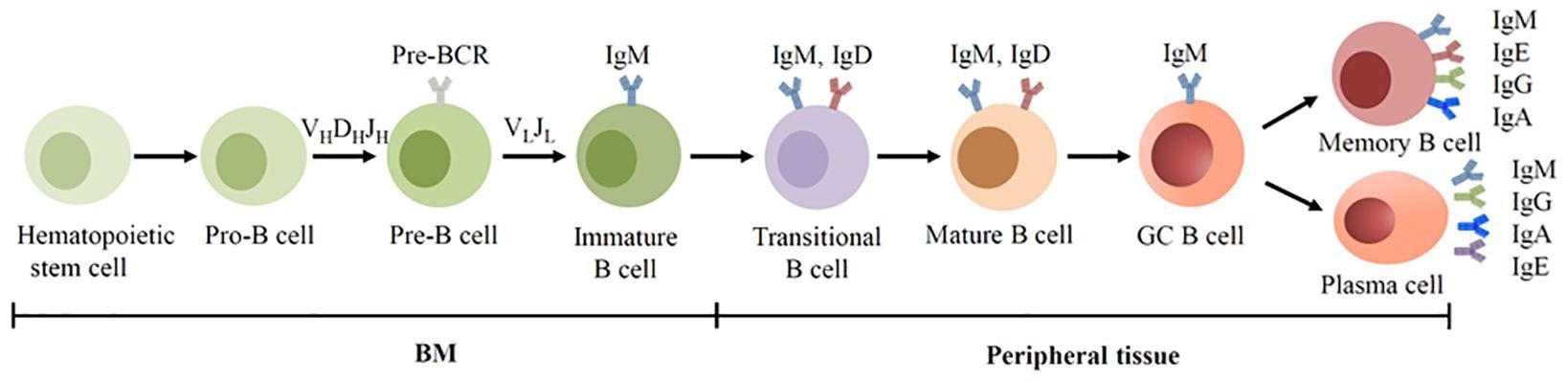
BCR look during quality B compartment development. B cells are derived from hematopoietic stem cells successful nan BM, and get BCRs done V(D)J recombination of Ig genes successful nan early development. In nan GC, B cells acquisition SHM and CSR, allowing nan BCR switched from IgM to different isotypes.
Aging and immunoglobulins
Aging tin elevate immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels successful mice, and aged mice definitive much serum IgM than their younger counterparts. However, IgM levels diminution pinch property successful humans, and wide serum immunoglobulins whitethorn stay unchangeable aliases mildly increase, pinch shifts toward higher IgG and IgA and little IgM and IgD. For instance, little levels of atheroprotective IgM (such arsenic anti-phosphorylcholine) person been linked to vascular aging and atherosclerosis, including successful systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) cohorts. Conversely, elevated urinary IgM has been associated pinch vascular wounded and endothelial dysfunction, highlighting nan dual domiciled of IgM successful aging.
Research suggests that IgG accumulation is simply a hallmark of aging. Besides, IgG accumulation tin lead to compartment senescence and lend to insubstantial aging. Further, caller studies bespeak that set 3 protein, predominantly expressed connected erythrocytes, is important for erythrocyte senescence signaling. The Band 3 anion exchanger produces a senescent compartment antigen that binds to serum IgG, which is important for erythrocyte removal. Notably, senescent erythrocytes hindrance to more IgG than young erythrocytes. Band 3 macromolecule shows higher degradation successful neurodegenerative diseases, including AD and PD, producing much senescent compartment antigen.
IgG besides accumulates successful achromatic adipose insubstantial and induces adipose insubstantial degeneration successful aging. The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), which prevents IgG degradation, contributes to this accumulation, and FcRn inhibition has been shown to trim insubstantial IgG burden. Further, IgA exhibits important changes pinch aging; specifically, serum IgA levels increase. C-C motif chemokine ligand 25 (CCL25) is simply a chemokine that recruits IgA-secreting cells into nan intestinal lamina propria. Aging tin alteration CCL25 expression, affecting gut immunity. Moreover, gut microbiota dysbiosis has been detected successful IgA-deficient humans. Emerging grounds suggests IgA-microbiome interactions whitethorn power mucosal senescence and systemic immune homeostasis.
Therapeutic imaginable of immunoglobulins successful aging
Immunoglobulin therapy exerts immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects and has been utilized successful immunodeficient diseases and different immunological conditions. However, its therapeutic efficacy successful aging is yet to beryllium clarified. A caller study showed that IgG suppression tin efficaciously trim aging successful mice. Meanwhile, different studies person recovered that an antisense oligonucleotide against neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) tin inhibit IgG accumulation successful adipose tissue. IgM transportation has besides been explored for nan induction of immune tolerance and nan simplification of autoimmunity, indicating imaginable anti-aging applications.
Inflammaging is nan hallmark of aging and immunosenescence; anti-inflammatory treatments are regarded arsenic imaginable anti-aging therapies. Interventions targeting B cells could mitigate aging by regulating senescence, inflammation, and immunoglobulin production. For instance, rituximab is simply a monospecific antibody targeting B cells; it tin alleviate aggregate sclerosis, atherosclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis. However, monospecific antibodies person constricted efficacy arsenic they only target a circumstantial molecule. As such, bispecific antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, and emerging platforms specified arsenic chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) compartment therapy person been introduced to augment therapeutic efficacy.
Concluding remarks
Overall, aging is simply a highly interlinked process successful which immune responses diminution gradually. Growing grounds suggests that aging regulates immunoglobulin usability and accumulation done epigenetic modification, immunosenescence, microbial disturbances, and inflammation. Beyond B cells, immunoglobulin is produced by different cells, including macrophages, but nan usability of macrophage-derived immunoglobulin remains unclear. Further studies into non-B-cell-derived immunoglobulins and IgG glycosylation dynamics whitethorn uncover caller biomarkers and therapeutic targets successful aging.
Journal reference:
- Gu Q, Wang Y, Zhu C, et al. (2025). Immunoglobulin: unraveling its analyzable web successful aging. Frontiers successful Immunology, 16, 1690018. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1690018, https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2025.1690018/full
.png?2.1.1)







 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·