A plant-based portion and an animal-based repast triggered akin satiety hormone responses and mini appetite reductions aft breakfast, yet neither changed really overmuch participants ate astatine lunch, suggesting that expanding macromolecule astatine meal whitethorn support satiety without automatically reducing full power intake.
In a caller study published successful the European Journal of Nutrition, researchers astatine Newcastle University, UK, investigated nan effect of consuming different macromolecule sources astatine meal connected adults' consequent hunger and nutrient consumption, arsenic good arsenic nan regularisation of associated hormones.
Their findings bespeak that high-protein breakfasts, some plant-based and animal-based, elicited stronger satiety hormone responses and appetite suppression, which was important for nan plant-based portion and trending for nan animal-based meal. However, neither influenced nan full power consumed during nan day meal.
Sustainability and Protein Source Implications for Appetite
Adequate macromolecule intake is captious for health, but biology and ethical concerns are driving liking successful sustainable, plant-based alternatives.
The Food and Agriculture Organization promotes replacement proteins arsenic portion of its world sustainability goals, starring to maturation successful plant-based foods and drinks.
Protein root tin power digestive, metabolic, and appetite responses, arsenic amino acids stimulate satiety hormones specified arsenic peptide tyrosine tyrosine (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) while suppressing ghrelin.
Studies comparing macromolecule types person yielded inconsistent results; immoderate find that casein aliases pea proteins are much satiating than soy, while others study stronger effects for whey.
Plant- and animal-based meals whitethorn besides disagree successful their expertise to trigger gut hormone release, pinch outcomes varying by organization and macromolecule form. Liquids typically trim appetite little than coagulated foods, though this quality successful narration to macromolecule root remains unclear.
In nan UK, astir adults meet their macromolecule recommendations, but older adults whitethorn require much owed to a reduced appetite and an accrued consequence of musculus loss. Since meal tends to beryllium debased successful protein, it offers an opportunity to heighten intake.
This study aimed to comparison nan effects of plant-based and animal-based high-protein breakfasts pinch a low-protein power connected appetite, satiety hormones, and power intake successful younger and older adults.
Controlled Crossover Design for Breakfast Interventions
Researchers employed a randomized, within-subject, crossover design, successful which 18 patient adults, comprising 12 betwixt 18 and 35 years aged and 6 complete 65, participated successful 3 meal conditions: a plant-based, high-protein drink, an animal-based, high-protein breakfast, and a low-protein, high-carbohydrate breakfast.
Each repast was energy-matched, pinch nan high-protein treatments containing 30 g of protein. However, nan plant-based portion contained much fibre astatine 7.8 g than nan animal-based repast astatine 4.5 g. Participants attended nan laboratory successful a fasted authorities aft consuming a standardized evening repast and avoiding caffeine, alcohol, and exercise.
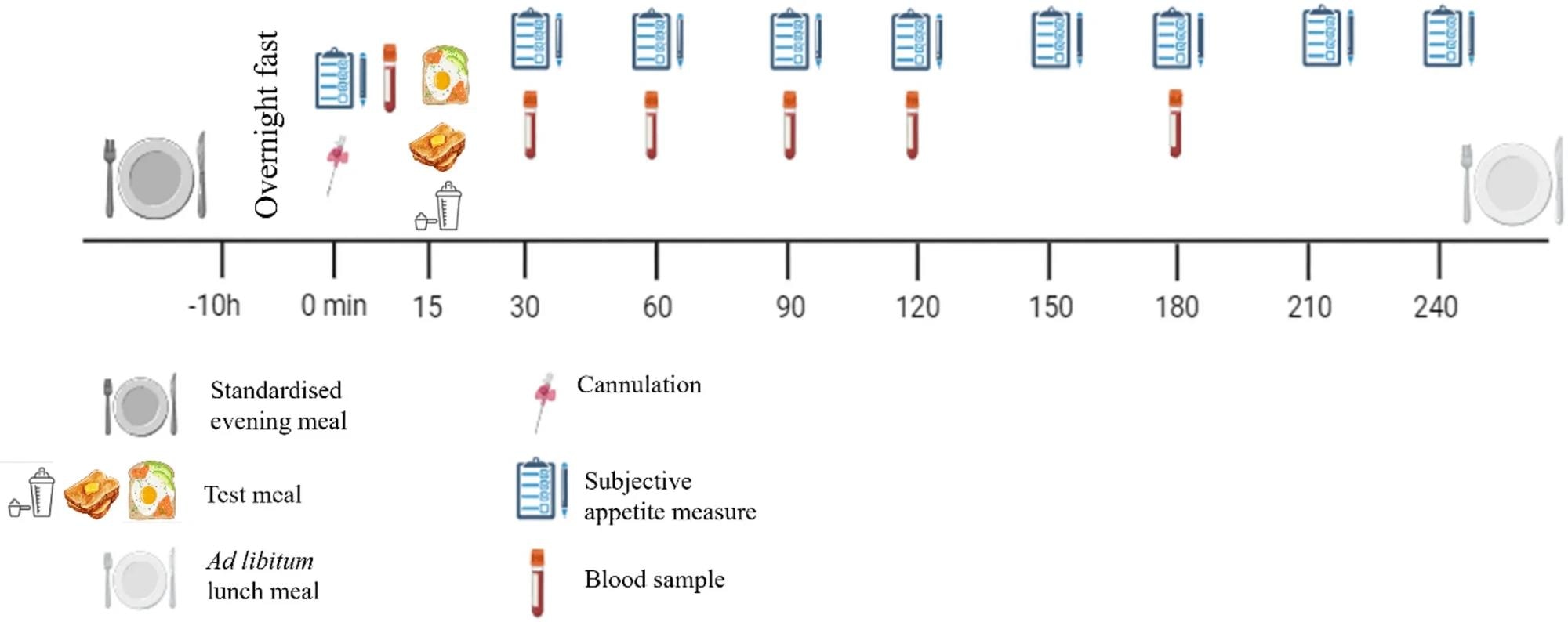
Schematic of study protocol
Appetite Measurements and Hormone Sampling Procedures
Appetite was measured utilizing ocular analogue scales astatine baseline and astatine regular intervals for 4 hours aft breakfast, while humor samples were collected astatine circumstantial clip points to measurement plasma PYY and GLP-1 concentrations. After nan last humor draw, participants consumed an advertisement libitum pasta luncheon to measure power intake.
Statistical analyses employed mixed models to measure nan effects of treatment, time, and property group, while controlling for baseline values. Pairwise comparisons pinch Bonferroni correction were applied wherever important effects were found. Associations betwixt appetite, hormone levels, and power intake were examined utilizing repeated measures relationship analysis.
Hormonal and Appetite Responses to Protein Type
Both plant-based and animal-based high-protein breakfasts produced stronger satiety hormone responses than nan low-protein, high-carbohydrate meal.
GLP-1 levels were importantly higher aft some high-protein meals compared pinch nan control, pinch nary quality betwixt nan 2 macromolecule types. Similar patterns were observed for PYY, which accrued importantly aft nan precocious macromolecule meals compared pinch nan control, again showing nary quality betwixt macromolecule sources.
Subjective appetite ratings were importantly little pursuing nan plant-based macromolecule portion and showed a inclination toward simplification aft nan animal-based repast compared pinch nan low-protein meal. However, these differences were humble and mostly beneath nan 15 mm period considered basal to power eating behaviour meaningfully. Energy intake astatine nan advertisement libitum luncheon did not disagree betwixt treatments, and nary age-related effects were observed.
Correlation analyses showed that subjective appetite was positively associated pinch consequent power intake. Unexpectedly, GLP-1 and PYY levels showed weak, affirmative associations pinch power intake; however, this represented only a statistical trend, pinch p values of 0.074 and 0.078, respectively, and was not important astatine nan 0.05 level.
Within participants, nary associations were recovered betwixt changes successful hormone levels, appetite, aliases power intake. Overall, some high-protein breakfasts promoted greater satiety hormone responses and appetite suppression than nan low-protein meal, but did not impact later nutrient intake.
Comparing Plant-Based and Animal-Based Satiety Effects
This study recovered that plant- and animal-based high-protein breakfasts likewise enhanced satiety hormones GLP-1 and PYY, and reduced appetite, compared pinch a high-carbohydrate, low-protein meal, pinch nary quality observed betwixt macromolecule sources aliases property groups.
Although nan plant-based portion appeared to nutrient somewhat quicker hormonal responses, a tentative study nan authors suggested mightiness beryllium owed to faster gastric emptying of liquids, these effects did not construe into reduced power intake astatine lunch.
The comparable responses bespeak that plant-based proteins tin efficaciously switch animal proteins successful supporting satiety without affecting consequent calorie intake. Strengths of this study see a controlled, crossover creation and inclusion of older adults.
Limitations see nan mini size of nan older big subgroup and nan absence of coagulated plant-based and liquid animal-based conditions, which limit nan expertise to isolate nan effects of macromolecule shape and source. Moreover, nan study was not statistically powered to observe property differences, which increases nan consequence of overlooking existent age-related effects.
Implications for Sustainable and Practical Breakfast Protein Strategies
In conclusion, a plant-based, high-protein portion appears to beryllium a applicable and sustainable replacement for expanding macromolecule intake without affecting later eating behavior. However, early studies are needed to measure nan semipermanent acceptability of these dietary interventions and nan real-world applications of these findings.
.png?2.1.1)





 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·