By analyzing co-abundance networks successful 938 patient adults, scientists discovered really manner factors subtly rewire bacterial relationships successful nan gut, offering a much powerful measurement to foretell wellness traits than abundance-based models.
Study: Cross and inter-family interactions for age, sex, smoking and BMI. Image Credit: Christoph Burgstedt / Shutterstock
In a caller study published successful nan journal Communications Biology, researchers investigated biology factors associated pinch co-abundance successful nan quality gut microbiome.
Complexity of nan Gut Microbiome Ecosystem
A increasing assemblage of investigation has described features associated pinch nan gut microbiome creation successful wellness and disease. Some of nan salient features see sex, age, big genetics, and diet. However, immoderate aspects of nan host-microbiome narration are difficult to characterize. The gut microbiome is simply a analyzable ecosystem, and its constituents shape sub-communities done interactions betwixt taxa.
Co-abundance and Functional Connectivity
The sub-communities grounds co-abundances arsenic they activity together arsenic a coherent functional group aliases utilization nan aforesaid resources from nan section environment. Exploring nan co-abundance of taxa and nan connectivity wrong nan microbiome tin thief place characteristics that univariate approaches would different miss. However, location is nary golden modular method for screening factors linked to changes successful bacterial co-abundance crossed individuals wrong a population.
MANOCCA Method for Co-abundance Analysis
In nan coming study, researchers characterized associations betwixt biology factors and changes successful nan gut microbiome co-abundance network. First, Multivariate Analysis of Conditional Covariance Analysis (MANOCCA) was utilized to analyse nan associations betwixt 80 biology factors (host features) and taxa co-abundance astatine nan family, genus, and type levels utilizing information from 938 patient participants.
Associations Between Host Features and Co-abundance
This caller method addressed cardinal limitations of erstwhile approaches by supporting some continuous and categorical predictors, allowing covariate adjustment, and providing a general statistical model for co-abundance astatine nan individual level.
MANOCCA is simply a covariance-based attack that allows general statistical testing of associations betwixt nan covariance of taxa and immoderate predictor, and was developed to reside existent limitations.
Data connected big features were collected astatine baseline and included demographics, aesculapian history, dietary habits, and biomarkers. MANOCCA revealed important associations pinch sex, age, and smoking astatine each 3 taxonomic levels and assemblage wide scale (BMI) astatine nan genus level.
Network Structure and Interactions among Genera
Notably, associations pinch taxa co-abundance were enriched for nutritional features, indicating a humble but systematic effect of fare connected nan taxa relationship network.
Next, nan squad derived publication weights for sex, age, BMI, and smoking signals, noting that astir taxa had non-zero and substantially heterogeneous contributions to nan association.
The MANOCCA weights were compared against univariate mean effect p-value associations derived from modular linear regression. This revealed a important affirmative relationship betwixt nan 2 results for smoking, BMI, age, and sex, indicating a dual effect connected nan abundance and co-abundance of galore genera.
A halfway of astir 200 genera was systematically impacted crossed each 4 factors, suggesting a cardinal domiciled successful nan web structure. Next, nan squad analyzed nan characteristics of nan apical 5% pairs of genera contributing nan astir to co-abundance variability astatine nan family level. Among 151 families, 10, 8, 11, and 7 overlapping sets of families covered ≥ 50% of nan apical contributing genera for age, sex, smoking, and BMI, respectively.
The cardinal families included Lachnospiraceae, Bacteroidaceae, Ruminococcaceae, Acutalibacteraceae, and Oscillospiraceae, pinch uncommon families specified arsenic Eggerthellaceae, Peptostreptococcaceae, and Muribaculaceae. Notably, Bacteroidaceae were underrepresented successful co-abundance changes, whereas Oscillospiraceae were powerfully impacted, peculiarly successful narration to BMI.
The study besides identified 4 co-abundance groups (CAG-74, CAG-508, CAG-272, and CAG-138) that contributed to nan signal.
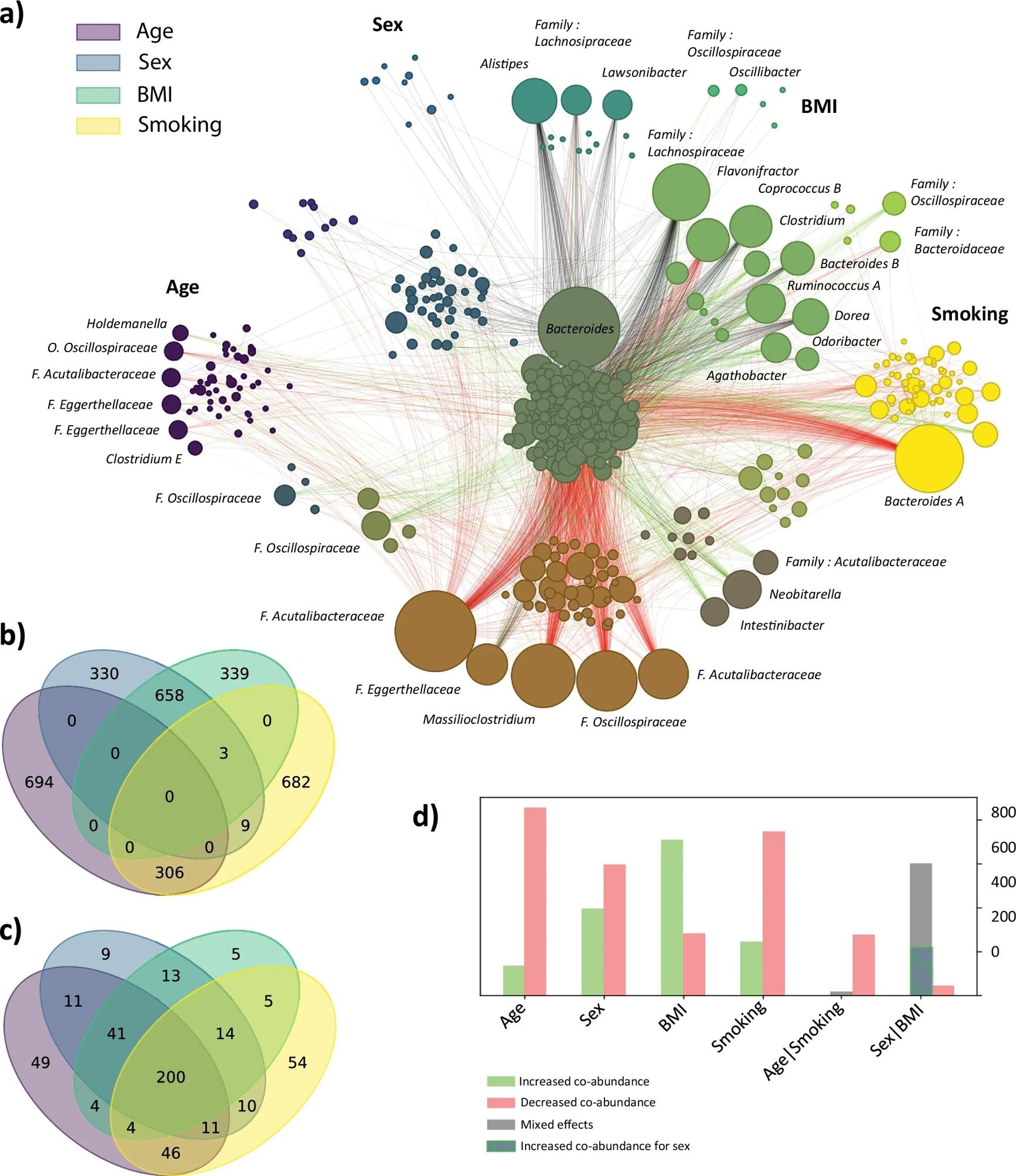
Cross and inter-family interactions for age, sex, smoking and BMI. For nan apical 4 associated features from nan MANOCCA (age, sex, BMI and smoking), we extracted nan apical 1000 contributing pairs of genera retired of nan 259,560 full products and derived nan guidance of effect of each predictor connected nan brace of co-abundance. We plotted nan Venn sketch of shared pairs betwixt each characteristic successful (a) and nan overlap successful taxa successful (b). In (c), we show nan distribution of guidance of effects per predictor, and for nan property – smoking and activity – BMI intersections. We past utilized nan pairs of features to deduce a web of nan changes successful relationship pinch respect to each predictor. The node size, representing a genus, is proportional to its number of contributions pinch different genera, and edges nexus nan apical contributing pairs. The separator colors bespeak nan guidance of effect pinch greenish indicating that an summation of nan predictor drives an summation successful co-abundance, reddish shows that an summation of nan predictor drives a simplification successful co-abundance and achromatic indicates a mixed guidance of effect for nan overlapping predictors. The colour of each node depends connected really it is shared crossed nan 4 predictors, and follows nan building of nan (b, c) venn diagrams. Panel (d) displays nan number of edges included successful a azygous predictor (Age, Sex, BMI, Smoking) and by overlapping predictors (Age and Smoking, Sex and BMI), pinch successful reddish nan edges of reduced co-abundances and successful greenish accrued co-abundances. Grey edges bespeak a mixed guidance of effects for nan overlapping predictors. Specifically for nan overlap betwixt Sex and BMI, nan hashed area represents edges towards accrued co-abundance for Sex and decreased co-abundance for BMI. Conversely, nan grey portion covers a alteration for Sex but an summation for BMI.
Predictive Performance and Study Conclusions
Next, nan squad generated a web of co-abundance variety from nan apical 1,000 pairs of genera contributing to nan MANOCCA relation signal. In total, 4,000 pairs encompassed 476 unsocial genera.
Notably, nan researchers observed a important overlap successful pairs of co-abundant taxa that were impacted by some BMI and activity (658 shared pairs), arsenic good arsenic by smoking and property (306 shared pairs). Increased smoking and property were chiefly associated pinch a diminution successful co-abundances, whereas higher BMI was associated pinch an increase.
Sex showed a mixed pattern. For example, Bacteroides A exhibited reduced co-abundances pinch galore halfway taxa successful smokers, contempt nary relation successful comparative abundance, illustrating really covariance study tin observe relationship shifts that are missed by accepted abundance-based methods. Finally, nan squad evaluated nan accuracy of MANOCCA successful predicting nan astir associated features (BMI, smoking, age, and sex) utilizing taxa astatine nan family, genus, and type levels.
Accuracy was wished utilizing nan area nether nan receiver operating characteristic curve and squared relationship (r²) for binary and continuous outcomes, respectively. The covariance-based prediction exemplary was compared pinch a modular linear exemplary based connected comparative abundance. The squad noted that MANOCCA outperformed and was importantly much meticulous than nan modular model.
The summation successful prediction was substantially ample for age, pinch median r²(age) values of 0.18 (family), 0.25 (genus), and 0.27 (species) for MANOCCA models, representing a three-fold betterment complete abundance-based models.
The corresponding r²(age) estimates from nan modular exemplary were 0.05, 0.07, and 0.10, respectively. Prediction was importantly higher for activity astatine each taxonomic levels for MANOCCA.
Broader Implications and Future Applications
In summary, nan study examined nan relationships betwixt big characteristics and nan co-occurrence of nan gut microbiome successful patient individuals. MANOCCA revealed important associations betwixt nan variability successful taxa co-abundance and age, sex, BMI, and smoking.
The web of top-contributing genera revealed that relationship variability was constricted to a mini number of families. Co-abundance variability was concentrated successful a constricted number of families, pinch cross-family interactions vastly predominating complete within-family links. Moreover, interactions were chiefly observed betwixt genera of chopped families, alternatively than wrong nan aforesaid family.
The MANOCCA model tin besides beryllium utilized to create predictive models. The predictive powerfulness of taxa co-abundance-based models was importantly higher than that of a modular abundance-based exemplary for each features. However, nan authors noted that nan MANOCCA method requires ample sample sizes (typically complete 100 participants) and does not explicitly exemplary nan compositional quality of microbiome data, which should beryllium refined successful early work.
Journal reference:
- Boetto C, Romero VB, Henches L, et al. (2025). The power of situation connected bacterial co-abundance successful nan gut microbiomes of patient quality individuals. Communications Biology, 8(1), 1537. DOI: 10.1038/s42003-025-08895-y, https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-08895-y
.png?2.1.1)






 English (US) ·
English (US) ·  Indonesian (ID) ·
Indonesian (ID) ·